Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220120-19
- Publication
- Ivanovics et al., 2021 - Embryonic exposure to low concentrations of aflatoxin B1 triggers global transcriptomic changes, defective yolk lipid mobilization, abnormal gastrointestinal tract development and inflammation in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
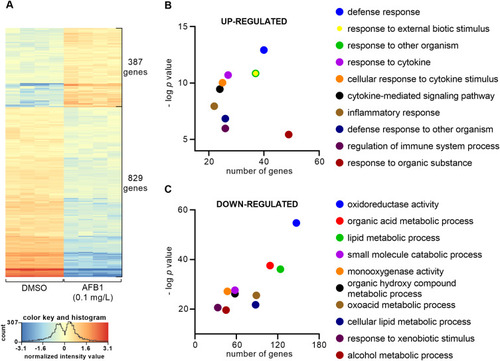
Embryonic exposure to AFB1 results in global gene expression changes in zebrafish larvae. (A) Heat map showing the differentially expressed genes between the control (DMSO) and the AFB1-exposed (0.1 mg/L) 120 hpf larvae. Data represent the normalized gene expression values of the four independent biological replicates per treatment. (B) Scatter plot showing the top 10 most significantly over-represented Gene Ontology terms among up-regulatedgenes in AFB1-exposed 120 hpf larvae. Y-axis represents the negative log (base 10) of the term significance (p-value). X-axis represents the number of genes associated with the term. (C) Scatter plot showing the top 10 most significantly over-represented Gene Ontology terms among down-regulated genes in AFB1-exposed 120 hpf larvae. Y-axis represents the negative log (base 10) of the term significance (p-value). X-axis represents the number of genes associated with the term. |
Reprinted from Journal of hazardous materials, 416, Ivanovics, B., Gazsi, G., Reining, M., Berta, I., Poliska, S., Toth, M., Domokos, A., Nagy, B., Staszny, A., Cserhati, M., Csosz, E., Bacsi, A., Csenki-Bakos, Z., Acs, A., Urbanyi, B., Czimmerer, Z., Embryonic exposure to low concentrations of aflatoxin B1 triggers global transcriptomic changes, defective yolk lipid mobilization, abnormal gastrointestinal tract development and inflammation in zebrafish, 125788, Copyright (2021) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ J. Hazard. Mater.