Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-211230-55
- Publication
- Huang et al., 2021 - An injury-induced serotonergic neuron subpopulation contributes to axon regrowth and function restoration after spinal cord injury in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
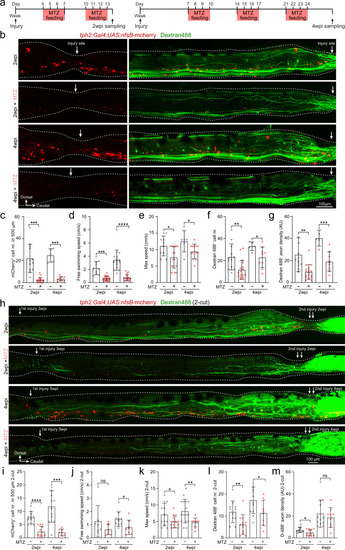
Injury-induced ISNs are indispensable for axon regrowth and locomotion recovery.
a Metronidazole (MTZ) treatment protocols used to genetically ablate mCherry+ ISNs after SCI using Tg(tph2:Gal4;UAS:nfsB-mCherry) line. b Immunohistochemistry images show the distribution of mCherry+ ISNs and Dextran 488+ retrogradely labeled axon-regrown spinal interneurons in 1-cut SCI fish with/without MTZ treatment. Injury sites are indicated by white arrows. c–g Ablation of ISNs by MTZ treatment prevents axon regrowth and locomotion recovery after SCI. Quantification of mCherry+ ISNs numbers in the region of 500 μm around the injury site (c); free-swimming speed (d); maximum swimming speed (e); retrogradely labeled axon-regrown spinal interneuron numbers (f) and regrown axon density (g) after SCI with/without MTZ treatment. h Immunohistochemistry images show the distribution of mCherry+ ISNs and Dextran 488+ retrogradely labeled axon-regrown spinal interneurons in two-cut SCI fish with/without MTZ treatment after the second injury. i–m Effect of ISNs ablation in 2-cut SCI model. Mean data of mCherry+ ISNs numbers in a 500 μm region covering the secondary injury site (i); free-swimming speed (j); maximum speed (k); retrogradely labeled axon-regrown spinal interneuron numbers (l) and regrown axon density (m) after the second injury with/without MTZ treatment. All data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, significant difference. For detailed statistics, see Supplementary Table 1. |