FIGURE
Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-211224-22
- Publication
- Choi et al., 2021 - Specialized neurons in the right habenula mediate response to aversive olfactory cues
- Other Figures
-
- Figure 1
- Figure 1—figure supplement 1.
- Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
- Figure 1—figure supplement 3.
- Figure 2
- Figure 3
- Figure 3—figure supplement 1
- Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- Figure 3—figure supplement 3
- Figure 3—figure supplement 4.
- Figure 4
- Figure 4—figure supplement 1
- Figure 5
- Figure 5—figure supplement 1
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
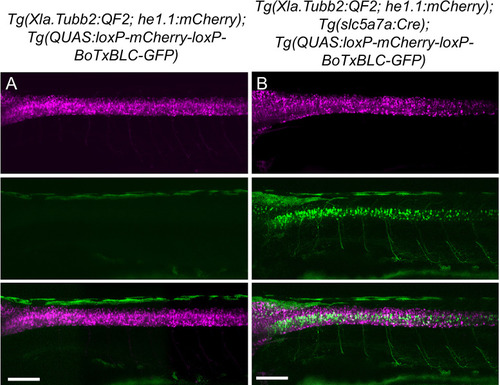
Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
|
Validation of intersectional strategy to inhibit cholinergic neurons using botulinum neurotoxin. Lateral views of (A) Tg(Xla.Tubb:QF2), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-BoTxBLC-GFP) and (B) Tg(Xla.Tubb:QF2), Tg(slc5a7a:Cre), Tg(QUAS:loxP-mCherry-loxP-BoTxBLC-GFP) larvae at 4 dpf. In the presence of Cre recombinase, cholinergic neurons in the spinal cord switch from mCherry to BoTxBLC-GFP expression, which inhibits their response to touch (refer to Video 1). Scale bars, 100 μm. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Elife