Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-211208-1
- Publication
- Mitsuzawa et al., 2021 - Reduced PHOX2B stability causes axonal growth impairment in motor neurons with TARDBP mutations
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
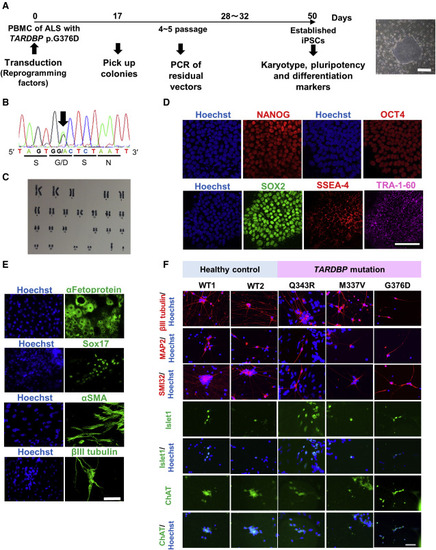
(A) Protocol for establishing iPSCs from the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of a familial ALS patient harboring the TARDBP p.G376D mutation. The panel shows the selected colony. Scale bar, 500 μm. (B) Reprogrammed PBMCs that formed colonies carried the same TARDBP p.G376D mutation as the familial ALS patient. The panel shows the heterozygous c.1127G > A change (black arrow) revealed by Sanger sequencing. (C) Karyotype analysis of iPSCs harboring TARDBP p.G376D. No karyotype abnormality was detected. (D) The established iPSCs expressed pluripotency markers as evidenced by immunocytochemistry. Scale bar, 100 μm. (E) Demonstration of the three germ layer differentiation capacity of iPSCs by immunocytochemistry. The endodermal markers α-fetoprotein and SOX17, the mesodermal marker αSMA, and the ectodermal marker βIII tubulin, were all expressed by iPSCs maintained in a basic fibroblast growth factor-free medium. Scale bar, 100 μm. See also Figure S1A. (F) Established iPSCs differentiated into MNs as verified by the expression of neuron-specific markers βIII tubulin, MAP2, and SMI32, and MN-specific markers Islet1 and ChAT. Scale bar, 50 μm. See also Tables S1 and S3. |