Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-211118-69
- Publication
- Matrone et al., 2021 - Nuclear S-nitrosylation impacts tissue regeneration in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
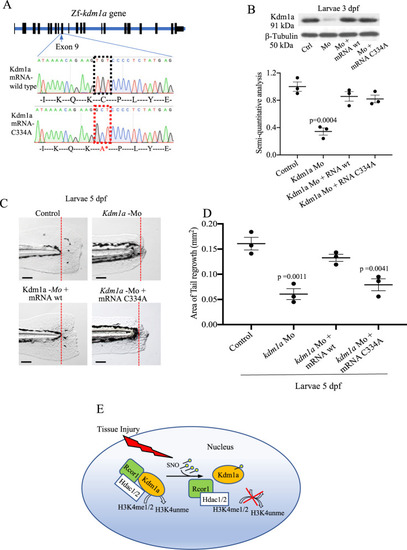
Modulation of Kdm1a S-nitrosylation during tailfin regeneration.
A Kdm1a mRNA C334A was generated by site-directed mutagenesis, replacing the aa Cys334 with Ala. B–D Zebrafish embryos injected with kdm1a morpholino (Mo), or co-injected with kdm1a Mo with kdm1a mRNA C334A or wild type. B Western blotting and semi-quantitative analysis showed the effective knockdown and rescue of kdm1a following the different treatments. β-tubulin was used as loading control. C, D Images and dot plot of tailfin regeneration following kdm1a modulation (p values vs. control). Scale bar measures 100 μm. E Working model. Tissue injury promotes the S-nitrosylation of the Cys334 of Kdm1a. S-nitrosylated Kdm1a detaches from the CoRest complex and loses its demethylase activity on H3K4. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test, p values indicate comparisons vs. control. N = 3 biological replicates. Data are presented as mean values +/− SEM. |