Figure 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-211029-84
- Publication
- Athapaththu et al., 2021 - Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Promotes Growth in Zebrafish Larvae by Inducing IGF-1 Expression via GABAA and GABAB Receptors
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
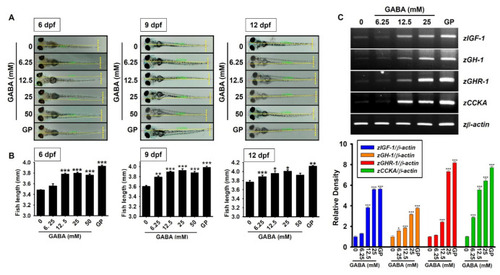
GABA promotes growth rate in zebrafish larvae through upregulation of growth-stimulating gene expression. Zebrafish larvae (n = 20) at three days post-fertilization (dpf) were treated with the indicated concentrations of GABA (0–50 mM). (A) Total body length was measured at 6, 9, and 12 dpf using a stereomicroscope (×4). β-Glycerophosphate (GP) at 4 mM was used as a positive control. (B) Graphs represent the total body length corresponding to each dpf. (C) Total mRNA was extracted at 9 dpf, and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was performed to measure the expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 (zIGF-1), growth hormone 1 (zGH-1), growth hormone receptor 1 (zGHR-1), and cholecystokinin A (zCCKA) genes. zβ-Actin was used as an internal control. Densitometry analysis was conducted to determine the expression level of each gene and expressed relative to that of β-actin (bottom). Significant differences among the groups were determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 vs. untreated zebrafish larvae). |