Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210325-65
- Publication
- Zheng et al., 2021 - Environmental chemicals affect circadian rhythms: An underexplored effect influencing health and fitness in animals and humans
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
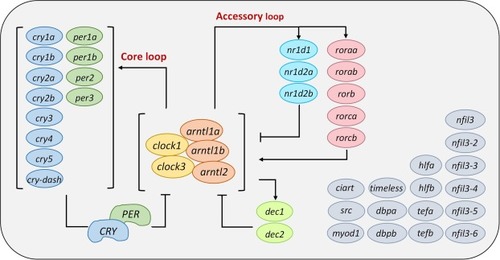
Circadian rhythm system in zebrafish and associated genes in the core and accessory loops. Our homologous alignments (based on current zebrafish genome annotation (GRCz11) in Ensembl database) identified 43 circadian genes. Multiple paralogues exist in zebrafish owing to the evolutionary whole-genome duplication events. Full name of each gene is shown in the Supplementary Material in Table S1. The core component is the clock/arntl heterodimer, which binds in the promoters of per and cry genes to induce its transcription, and the physical binding of PER and CRY proteins will interact to inhibit clock/arntl heterodimer transcription, thereby forming a core negative feedback loop. Nuclear receptor genes, nr1ds and rors, are also involved in as accessory loops. The former is regulated by a negative and the latter by a positive feedback regulation mechanism. Circadian genes in grey color indicate that their mechanisms of action are not yet entirely understood. |