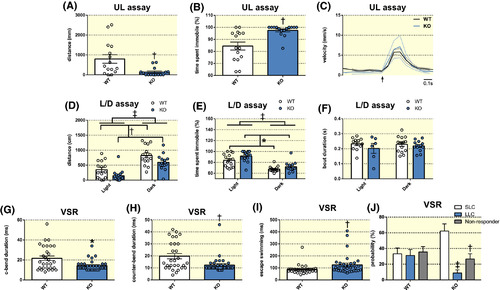
Effects of histamine receptor H3 (hrh3) deletion on larval behaviour. A, Total distance travelled, (B) time spent immobile and (C) average velocity during beat‐glide swimming of larval hrh3−/− (KO) and corresponding wild‐type (WT) fish in the larval unstimulated locomotion (UL) assay. The arrow in (C) indicates the onset of the swimming bout. n = 15/group. Mann‐Whitney U test. †P < .01 vs WT. D, Total distance travelled, (E) time spent immobile and (F) average swim bout duration in the larval light/dark transition (L/D) assay. n = 15/group. Two‐way ANOVA. Significant main effects are indicated in the graph. ‡P < .001, †P < .01, *P < .05. G‐I, Visual startle response (VSR) test. Larval KO fish displayed (G) shorter c‐bend durations, (H) shorter counter‐bend durations and (I) enhanced escape swimming compared to corresponding WT fish. n = 15/group. Mann‐Whitney U test. †P < .01, *P < .05 vs WT (J) In addition, KO fish were more likely to perform short latency c‐bends (SLC) compared to long latency c‐bends (LLC) and not responding at all. n = 15/group. Two‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post‐hoc test. ‡P < .001, †P < .01 vs SLC/KO. Data are presented as mean ± SEM
|

