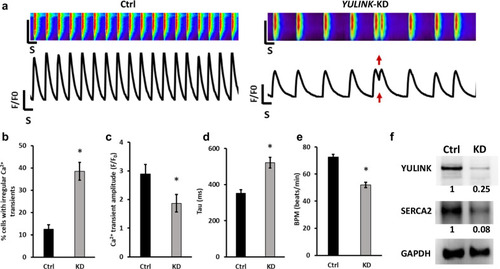
Assessment of arrhythmia and irregular Ca2+ regulation in YULINK KD iPSC-derived human cardiomyocytes. a Representative Ca2+ scans and spontaneous Ca2+ transient in control and YULINK KD iPSC-derived human cardiomyocytes. Red arrows indicate abnormal arrhythmia-like Ca2+ waveforms observed in YULINK KD cardiomyocytes. b Percentages of the irregular Ca2+ transients in control and YULINK KD iPSC-derived human cardiomyocytes (n = 40). c Bar graph comparison of Ca2+ transient amplitude of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes for control and YULINK KD confirmed that YULINK KD human cardiomyocytes exhibited a lower Ca2+ transient amplitude (n = 40). d The time constant for Ca2+ decay (Tau) of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes for control and YULINK KD showed that the time constant for Ca2+ decay was significantly larger in YULINK KD than in control iPSC-derived human cardiomyocytes (n = 40). e Quantification of spontaneous beating rate of control and YULINK KD human cardiomyocytes (n = 40). (*p < 0.05, Student’s t test). f Human cardiomyocytes were subjected to YULINK KD using YULINK-shRNA and the effects on YULINK and SERCA2 expression were assayed by Western blot
|

