|
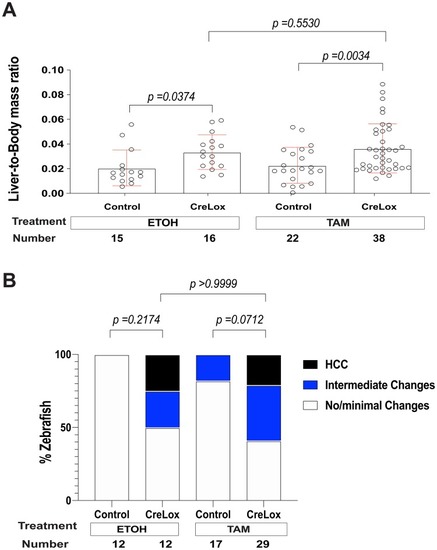
Switching on additional activated β-catenin in adult zebrafish does not increase HCC penetrance. CreLox [Tg(fabp10a:CreERT2); Tg(fabp10a:flox-pt-β-cat)] zebrafish and control siblings lacking either the Cre driver or lox-switch transgene [Tg(fabp10a:flox-pt-β-cat) and Tg(fabp10a:CreERT2), control], were treated with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (TAM) or vehicle (ethanol, EtOH) at 3 mpf. Livers were weighed and examined microscopically 6 months later. (A) Scatter plot showing liver mass normalized to total body mass, ±s.d. P-values were obtained using ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test. Data from four experiments were pooled. (B) Stacked bar graph showing the percentage of zebrafish per tested group categorized as no/minimal changes, intermediate changes, or HCC. P-values derived using Fisher's exact test, comparing samples with and without HCC. Data from three experiments were pooled.
|