Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-190923-5
- Publication
- Wang et al., 2019 - A long noncoding RNA cluster-based genomic locus maintains proper development and visual function
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
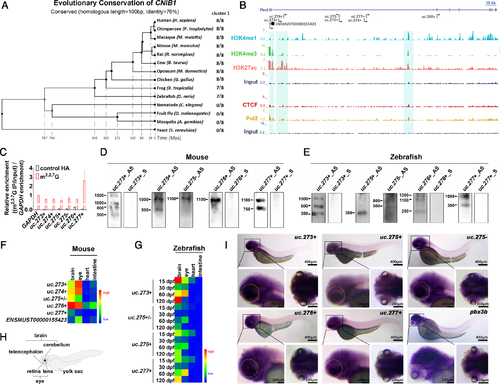
Characteristics of CNIB1. (A) Phylogenetic tree of CNIB1 genomic locus in the 14 indicated species. (B) Comprehensive view of multiple peak distributions of promoter marker (H3K4me3), enhancer markers (H3K27ac and H3K4me1), insulator marker CTCF and Pol2 binding sites on CNIB1 locus suggest these lncRNAs in CNIB1 are transcribed as independent lncRNAs. The three regions highlighted in turquoise were predicted to be the transcription start sites for CNIB1 lncRNAs. Scale bar: 10kb. (C) Cap assay of indicated CNIB1 lncRNAs. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-m2,2,7G antibody or control anti-HA, followed by RT-qPCR detection. Bar plots represent relative enrichment of RNAs immunoprecipitated by the antibody and normalized to GAPDH. (D, E) Northern blotting of CNIB1 lncRNAs in the eyes of mouse (D) and of zebrafish (E) both at 2 months. (F, G) Heatmap of the expression level of CNIB1 lncRNAs. qPCR assays were performed using the brain, eye, heart, and intestine tissues from three 10-week old male mice (F) and six zebrafish (G) at the indicated developmental time points (15, 30, 60 and 120 dpf, respectively), normalized to β-actin. (H) Schematic representation of zebrafish. (I) Whole-mount ISH of five indicated CNIB1 lncRNAs (uc.273+, uc.275+, uc.275-, uc.276+, uc.277+) and pbx3b using corresponding antisense digoxigenin-labeled probes in larval zebrafish (n = 8). The yellow dotted oval marks the area where the eye of zebrafish is located. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |