Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-190604-33
- Publication
- DeLaurier et al., 2019 - hdac4 mediates perichondral ossification and pharyngeal skeleton development in the zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
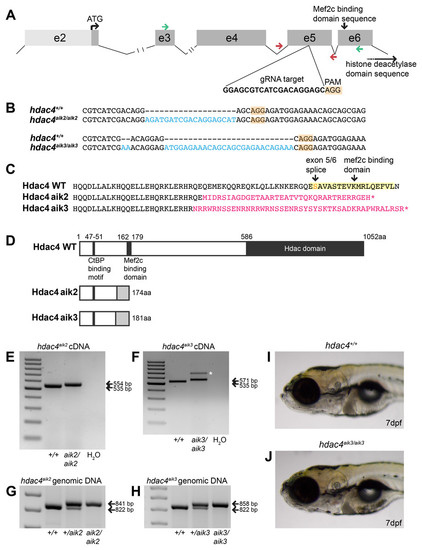
Overview of CRISPR strategy and generation of hdac4mutant lines.(A) Genomic structure of hdac4 showing gRNA target associated with the protospacer adjacent motif (5′-NGG, PAM) upstream of the Mef2c binding domain sequence. The histone deacetylase domain sequence is at the 3′ end of the gene. Green arrows indicate forward (exon 3F) and reverse (exon 6R) primers for RT-PCR and sequencing of cDNA. Red arrows indicate intronic genotyping primers (hdac4 F6, hdac4 R6) flanking exon 5. Intron 2/3 and 3/4 not to scale, indicated by hash marks. (B) Alignment of wild-type (hdac4+/+) with mutant cDNA sequence showing nucleotide insertions (blue) in hdac4aik2/aik2 and hdac4aik3/aik3 mutants in exon 5. (C and D) Insertion of nucleotides results in reading frame shifts causing aberrant protein sequences (magenta in C, grey boxes in D), loss of the Mef2c binding domain (indicated in yellow in C), and premature termination of the protein sequence (asterisk in C indicates stop codon). (E and F) RT-PCR showing hdac4 cDNA is spliced correctly in mutants and there is no evidence of splice variants. The wild-type cDNA product is expected to be 535 bp and mutant bands are 554 bp (E) and 571 bp (F). The larger band in hdac4aik3 mutants (indicated by white asterisk in (F) was sequenced and determined to be identical to the lower band. (G and H) Genomic DNA samples were genotyped by PCR and show differences in band sizes indicating mutant (841 bp hdac4aik2 mutant, 858 bp hdac4aik3 mutant), wild-type (822 bp), and heterozygous fish (mutant and wild-type bands). (I and J) At 7 dpf, mutant hdac4aik3 fish (J) have no apparent external abnormalities compared to wild-type siblings (I). H2O = negative control. 100 bp ladder. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Days 7-13 |