Fig. 2
|
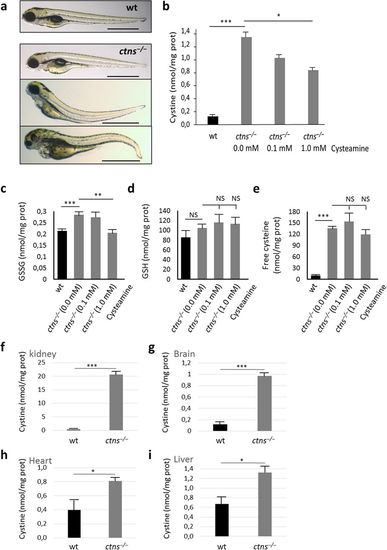
(a) Morphology of wild-type and ctns−/− larvae at 4 dpf. Wild-type larva shows normal morphology, while mutant ctns−/− larvae show various degrees of developmental delay and deformity: upper larva show signs of growth retardation in the form of slightly bigger yolk, bulging heart and bent-down head, while the middle and lower larvae show mild and severe deformity, respectively (bars = 1 mm). (b) Cystine content in homogenates of 6 dpf wt or ctns−/− zebrafish larvae. ctns−/− larvae were either free of treatment (N = 133) or subjected to 0.1 or 1.0 mM of cysteamine in the swimming water (N = 111 and 121 larvae, respectively). Comparison was performed with wt larvae (N = 191). (c) Oxidized glutathione (GSSG) content in homogenates of 6 dpf wt or ctns−/− zebrafish larvae (same conditions and larval numbers as cystine). (d) Total glutathione (GSH) content in homogenates of 6 dpf wt or ctns−/− zebrafish larvae. ctns−/− larvae were either free of treatment (N = 80) or subjected to 0.1 or 1.0 mM of cysteamine in the swimming water (N = 108 and 104 larvae, respectively). Comparison was performed with wt larvae (N = 158). (e) Free cysteine content in homogenates of 6 dpf wt or ctns−/− zebrafish larvae (same conditions and larval numbers as GSH). (f–i) Cystine content in homogenates of 8-month-old adults (Kidney, brain, heart and liver, respectively) (N = 3 of each genotype). Concentrations of cystine and other thiol compounds were expressed as nmol/mg protein. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Day 4 to Adult |