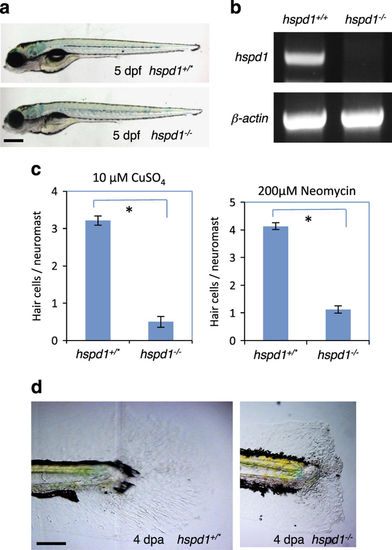
hspd1 mutants display deficient regeneration of lateral line hair cells and caudal fins. (a) The morphology of hspd1 mutants looks normal except for the lack of an inflated swim bladder at 5 dpf. hspd1+/* are wild-type or heterozygous fish. hspd1−/− are confirmed homozygous mutant fish. (b) RT-PCR analysis of hspd1 mRNA expression. The retroviral DNA is inserted in the first intron of the hspd1 gene, and the first exon is noncoding. The primers used for hspd1 knockdown analysis bind to the exon 3 and exon 6. β-actin is used as an internal reference. (c) Hair cell regeneration analysis using CuSO4 or neomycin to ablate hair cells. Concentrations are as labelled. The reduction is significant for both treatments (n=10, P<0.001 for both copper and neomycin). Asterisks in the graphs indicate a significant difference between the control and mutant embryos. (d) Caudal fin regeneration is deficient in hspd1−/− mutants. The end of the tail was removed at 3 dpf, and regeneration evaluated at 4 dpa, and then phenotype was correlated to genotype. Defects in fin regeneration were observed in 1/21 of hspd1+/* embryos, and 14/18 of hspd1−/− embryos. Bars = 500 μm in a and 200 μm in d. dpa, day post amputation; dpf, day post-fertilisation; RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase PCR.
|

