Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-171016-27
- Publication
- Ciarlo et al., 2017 - A chemical screen in zebrafish embryonic cells establishes that Akt activation is required for neural crest development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
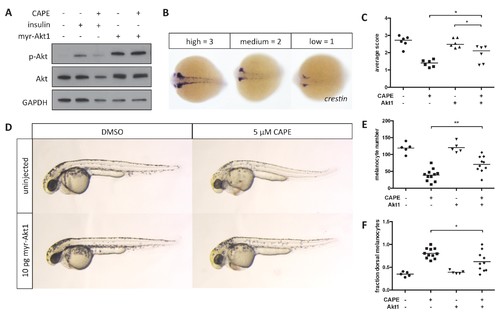
Myr-Akt1 rescues neural crest defects caused by CAPE. (A) Injection of myr-Akt1 RNA results in high phospho-Akt in heterogeneous neural crest cultures regardless of CAPE treatment. The same result was observed in four independent experiments. (B) Scoring system for crestin in situ hybridization. (C) Myr-Akt1 injection increases crestin expression in CAPE-treated embryos. Each point represents the average score of embryos from a single clutch (23–66 embryos per clutch). Three independent experiments are shown. (D) Morphology and pigmentation of CAPE-treated and injected embryos at 2 dpf. Images are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Myr-Akt1 increases melanocyte number in CAPE-treated embryos. Trunk melanocytes were counted as in Figure 4. Each point represents one embryo from the same clutch; bars indicate mean. (F) Myr-Akt1 reduces the fraction of dorsal melanocytes in CAPE-treated embryos. *p<0.05, **p<0.005, (C) paired t-test, (E–F) unpaired t-test. Figure 5—figure supplement 1 shows the effect of PI3K inhibitors on crestin:EGFP expression in vitro and the effect of myr-Akt1 on CAPE-induced embryonic defects. |