Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170123-13
- Publication
- Miranda-Rodríguez et al., 2017 - RhoA/ROCK pathway activity is essential for the correct localization of the germ plasm mRNAs in zebrafish embryos
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
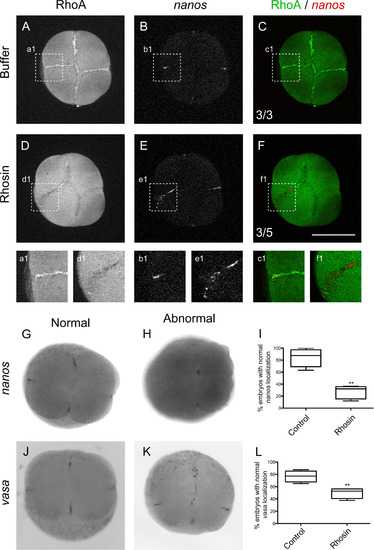
RhoA Inhibition with Rhosin affects vasa and nanos mRNAs localization at the cleavage furrow in 4-cell stage zebrafish embryos. Embryos were injected with control media (A–C, a1, b1, c1, G and J) or with RhoA inhibitor Rhosin (D–F, d1, e1, f1, H and K). (A and D) RhoA immunolocalization. (B and E) nanos mRNA fluorescent in situ hybridization. (C and F) Image superimposition of double labeled embryos with RhoA immunolocalization (green) and nanos fluorescent in situ hybridization (red) Embryos injected with control media show normal nanos localization (n=3); meanwhile Rhosin injected embryos showed abnormal localization (n=5). (G) nanos normal localization and (H)abnormal localization of nanos at the center of the injected embryo with Rhosin. vasa mRNA in situ hybridization normal localization (J) and abnormal vasa localization in injected embryos with Rhosin (K). (I) The differences observed in the pattern of normal localization of nanos in control (n=80) and Rhosin injected embryos (n=97) were quantified in 5 independent experiments. The error bars represent the standard error of the mean (** p<0.01). (L) Differences observed in the normal localization pattern of vasa between control (n=79) and Rhosin injected embryos (n=83) were quantified from 3 independent experiments. The error bars represent the standard error of the mean (** p<0.01). Scale bar 250 µm. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Antibody: | |
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | 4-cell |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | 4-cell |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 421(1), Miranda-Rodríguez, J.R., Salas-Vidal, E., Lomelí, H., Zurita, M., Schnabel, D., RhoA/ROCK pathway activity is essential for the correct localization of the germ plasm mRNAs in zebrafish embryos, 27-42, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.