Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150609-14
- Publication
- Love et al., 2015 - Rest represses maturation within migrating facial branchiomotor neurons
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
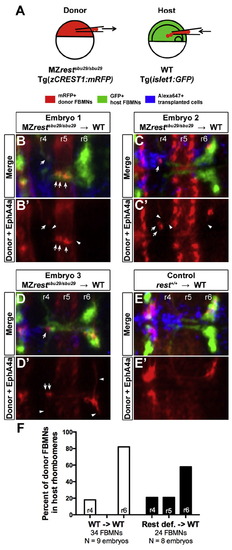
Cell transplantation reveals that Rest function is required specifically in FBMNs for their complete migration. (A) Schematic of transplantation approach. Blastula stage donor-derived MZrestsbu29/sbu29 mutant cells were transplanted into the hindbrain primordia of gastrula stage wild type hosts. To enable targeting of the hindbrain primordium, each host embryo was positioned with the dorsal shield at a 45° angle as indicated. (B–E) Average intensity projection confocal images (dorsal views, anterior to the left) of 48 hpf transplanted and immunolabeled embryos. Donor-derived FBMNs and EphA4a staining (r3 and r5) in red, host FBMNs in green, and all transplanted cells in blue (Alexa Fluor 647-labeled). (B′–E′) Red channel only, showing position of donor-derived FBMNs. Arrows indicate FBMNs that did not migrate to r6; arrowheads indicate long projections extended by MZrestsbu29/sbu29 donor-derived cells. (F) Percent of total donor FBMNs from wild type or MZrestsbu29/sbu29 embryos located in r4, r5, or r6 after transplantation into wild type hosts. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 401(2), Love, C.E., Prince, V.E., Rest represses maturation within migrating facial branchiomotor neurons, 220-35, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.