Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140214-3
- Publication
- Jacob et al., 2014 - Valproic Acid silencing of ascl1b/ascl1 results in the failure of serotonergic differentiation in a zebrafish model of Fetal Valproate Syndrome
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
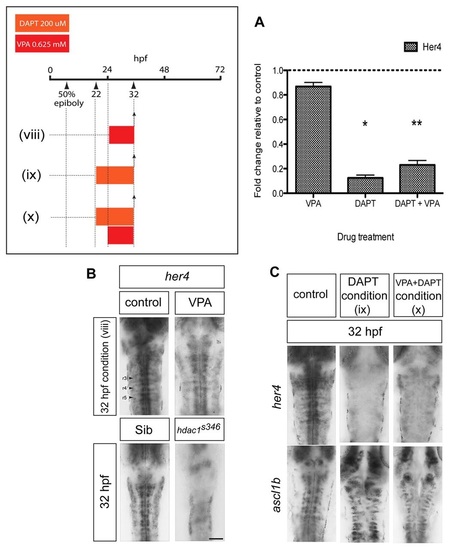
VPA treatment exposes cryptic transcriptional repression of ascl1b by basal levels of Notch signalling. (A) Quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR showing that VPA mildly reduces her4 expression, whereas DAPT strongly reduces her4 expression to between 12% and 23% of control levels (*P=0.017, **P=0.001). (B) Short duration (8 hour) treatment with VPA [condition (viii)] does not upregulate her4 expression at 32 hpf (n=12/12). Downregulation of her4 expression in hdac1s436 mutant hindbrain at 32 hpf (n=5/5). Scale bar: 50 µm. (C) Concomitant blockade of Notch signalling using the γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT prevents the downregulation of ascl1b by VPA. Loss of her4 expression in DAPT-treated embryos [conditions (ix) and (x)] (upper panels) (n=35/35). Persistence of ascl1b expression in embryos treated with VPA and DAPT [condition (x)] (n=23/23). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Conditions: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Prim-15 |