Fig. S7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-131218-37
- Publication
- Targoff et al., 2013 - Nkx genes are essential for maintenance of ventricular identity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
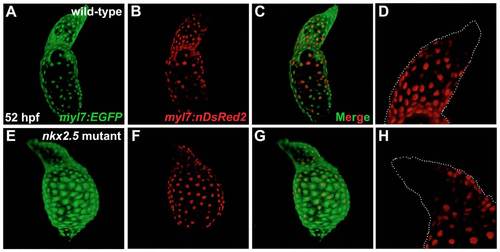
Developmental timing assay indicates late-differentiating cells added to the arterial pole of the nkx2.5 mutant heart. |