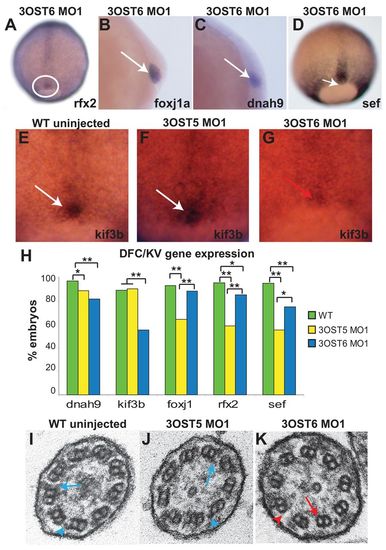
3-OST-6 regulates distinct cell signaling pathways to control cilia motility. (A-D) In contrast to diminished expression in 3-OST-5 MO-injected embryos (Fig. 3), 3-OST-6 MO1-injected embryos had normal expression of ciliogenic transcription factors rfx2 (A; n=74) and foxj1a (B; n=84). Motor molecule dnah9 (C; n=60) and the FGF-response gene sef (D; n=39) were also normally expressed in 3-OST-6 MO1-injected embryos. (E-G) Motor molecule kif3b mRNA normally expressed in the DFCs of 90% epiboly uninjected embryos (E, white arrow; n=79) and 3-OST-5 MO1-injected embryos (F, white arrow; n=48) was diminished in 3-OST-6 MO1-injected embryos (G, red arrow; n=38). (H) Percentages of embryos with normal levels of DFC expression of each marker gene in WT uninjected (green), 3-OST-5 MO1-injected (yellow) and 3-OST-6 MO1-injected (blue) embryos. *P<0.05, **P<0.001. The data represent a compilation of at least three independent experiments. (I-K) Electron micrographs showing cross-sections of cilia in the KV. Inner (blue arrows) and outer (blue arrowheads) dynein arms were visible in WT (I; n=3 embryos) and 3-OST-5 MO1-injected embryos embryos (J; n=4 embryos; P<1 compared with WT). By contrast, inner (red arrow) and outer (red arrowhead) dynein arms were largely absent in 3-OST-6 morphants (K; n=4 embryos; P<0.0018 compared with 3-OST-5 MO1 and WT).
|

