Fig. 9
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130218-32
- Publication
- Janssens et al., 2013 - Matrix metalloproteinase 14 in the zebrafish: an eye on retinal and retinotectal development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
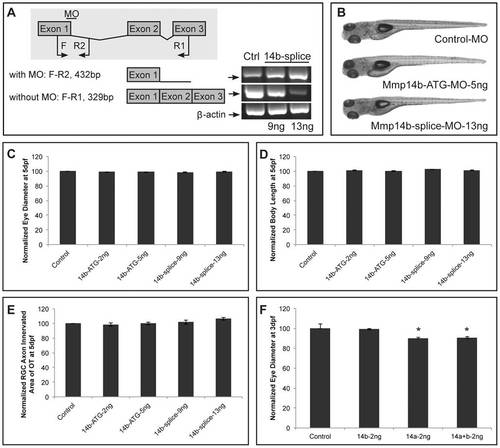
Mmp14b is not involved in retinal development. A RT-PCR analysis of Mmp14b-splice MO-injected embryos reveals efficient splice blocking, resulting in a dose-dependent increase in aberrantly spliced mmp14b mRNA. Since the splice MO targets intron 1 of mmp14b, which is 11 kb large, 2 different primer sets were used to visualize the splice blocking. Primer set F-R1 generates a fragment spanning exon 1 to 3 to detect correctly spliced transcripts (329 bp), and primer set F-R2 generates a fragment that spans exon 1 and part of intron 1 to detect aberrantly spliced transcripts (432 bp). The house keeping gene β-actin was used as a loading control. B Mmp14b knockdown using either the Mmp14b-ATG MO (5 ng) or the Mmp14b-splice MO (13 ng) in combination with the p53 MO does not affect normal embryonic morphogenesis at 5 dpf. C-E Quantitative analysis of eye size (C), total body length (D) and tectal area innervated by RGC axons (E) at 5 dpf, shows a normal eye diameter and tectal arborization area in Mmp14b morphant embryos using both the Mmp14b-ATG MO and Mmp14b-splice MO as compared to control embryos (n = 65 from 3 independent experiments)., F Combined knockdown of Mmp14a and Mmp14b (both injected at 2 ng) does not aggravate the eye defects observed after single Mmp14a knockdown in 3 dpf embryos (n = 70 from 3 independent experiments). Data are represented as mean ± SEM (*p<0.05, Student′s t-test). Dpf, days post fertilization; F, forward; MO, morpholino; R, reverse. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 5 |