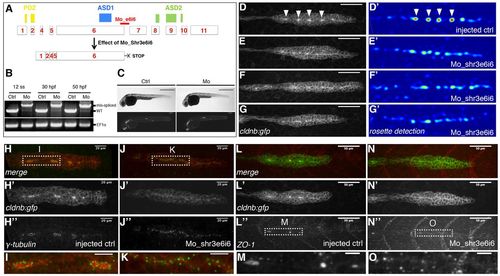
Shroom3 knockdown blocks apical constriction and rosette assembly in the migrating pLLP. (A) Schematic showing the position of Mo_Shr3e6i6. (B) RT-PCR with shr3- (top) and EF1α-(bottom) specific primers on zebrafish embryos injected with Mo_Shr3e6i6 or with water (ctrl) showing that Mo_Shr3e6i6 efficiently generates an alternative splice variant (mis-spliced) by blocking the excision of intron 6, potentially leading to a truncated protein lacking the poly-proline and ASD2 domain (A). (C) transmitted light and fluorescence pictures of embryos injected either with water (left) of with Mo_Shr3e6i6 (right). (D-G′) Live images of the primordium of cldnb:gfp embryos injected with water (D,D′) or with Mo_Shr3e6i6 (E-G′) showing that knocking down Shroom3 function blocks the assembly of apically constricted rosettes (arrowheads in D). D′-G′ are the corresponding detection response images (using Jet, a blue-to-red colour map) obtained from our rosette detector (see Materials and methods). (H-O) Side views of the primordium of 36 hpf cldnb:gfp embryos immunostained for the centrosomal marker γ-tubulin (H-K) or the tight-junction protein ZO1 (L-O). I, K, M and O are close-up views of the boxed areas in H, J, L′′ and N′′, as indicated. Scale bars: 50 μm in D-G′ ;10 μm in I,K,M,O.
|

