Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120216-17
- Publication
- Mishima et al., 2012 - Translational inhibition by deadenylation-independent mechanisms is central to microRNA-mediated silencing in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
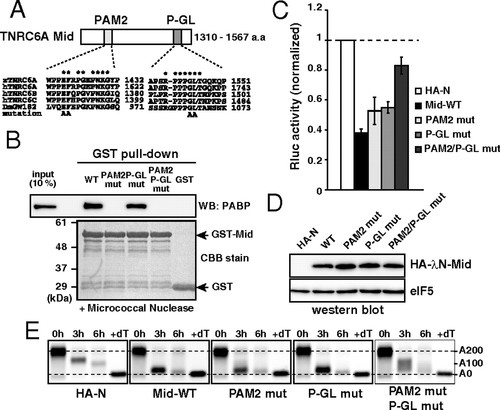
The Mid domain of TNRC6A represses translation via two motifs. (A) Schematic representation of the Mid domain of zebrafish TNRC6A. The two conserved motifs (PAM2 and P-GL) are shown. Sequence alignments of each motif comparing zebrafish TNRC6A, human TNRC6 proteins, and fly GW182 are shown. Conserved residues are marked with asterisks. Alanine substitutions introduced in the current study are shown on the bottom. (B) GST-pulldown assay detecting interaction between the GST-Mid domain and zebrafish PABP. A total of 10% of embryonic lysate was loaded as an input. PABP was detected using Western blotting (Upper). GST fusion proteins were visualized using CBB stain (Lower). (C) The results of the tethering assay with TNRC6A Mid domain mutants. The data were collected and are shown as described in Fig. 1C. (D) Western blot detecting HA-λN-tagged Mid domain proteins. The membrane was probed with anti-eIF5 antibody as a control. (E) The poly(A) tail analysis of the injected Rluc-BoxB-pA reporter mRNA using RNaseH digestion and northern blot at 0, 3 and 6 hours. The lane +dT shows a completely deadenylated fragment (A0). |