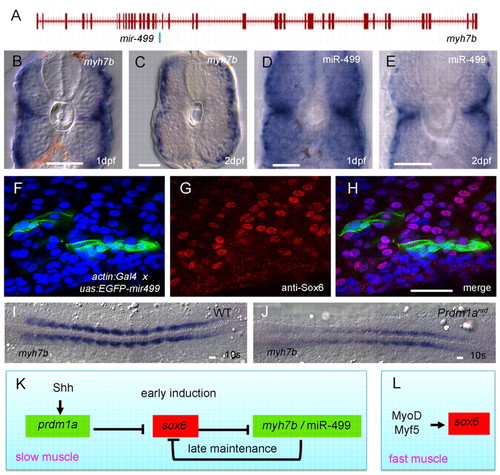
Prdm1a promotes the spatially restricted expression of myh7b and mir499, which is sufficient to repress sox6 translation. (A) Exon-intron structure of the myh7b gene showing the location of mir499 in intron 18. (B-E) Transverse sections of wild-type embryos hybridised with probes for myh7b or miR-499 transcripts, both of which are restricted to the superficially located slow-twitch fibres and the medially located muscle pioneers, a subset of the slow-twitch lineage. (F-H) Sagittal optical sections of a 24 hpf Tg(actin:GAL4) embryo injected with an EGFP-mir499 construct under UAS control; fibres expressing the construct (F, green) show significant reduction in nuclear accumulation of Sox6 protein (G, red) as revealed by the merged image (H); nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (I,J) Flat mounts of 10-somite stage wild-type and prdm1anrd mutant embryos hybridised with probe for myh7b, showing strong downregulation in the absence of Prdm1a function. (K,L) Gene regulatory network underlying the specification and maintenance of slow-twitch and fast-twitch muscle lineages in zebrafish. Scale bars: 20 μm.
|

