Fig. 3
|
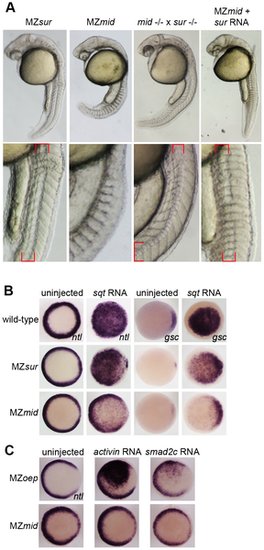
sur retains more Nodal transduction capability than mid. (A) Genetic interactions between the sur and mid alleles, demonstrating the ability of sur to partially rescue the loss of notochord caused by mid. Lower panels are enlargements showing the structures of the notochords at 24 hpf; red brackets indicate notochord domains. (B) Nodal overexpression in maternal-zygotic FoxH1 mutants. 50 pg sqt RNA was injected into wild-type, MZsur, and MZmid embryos at the one-cell stage, and embryos were assayed for Nodal target gene expression at 30–40% epiboly. Note the greater ability of MZsur embryos to respond to ectopic sqt compared to the MZmid response. (C) The mid mutation perturbs activin-like signaling. MZoep and MZmid embryos were injected with RNA encoding either a Xenopus activin homologue (2.5 pg) or an activated form of mouse Smad2 (100 pg). Responses were assayed by observing ntl expression at 30–40% epiboly. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | 30%-epiboly |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |