Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110324-27
- Publication
- Sheets et al., 2011 - Ribeye is required for presynaptic CaV1.3a channel localization and afferent innervation of sensory hair cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
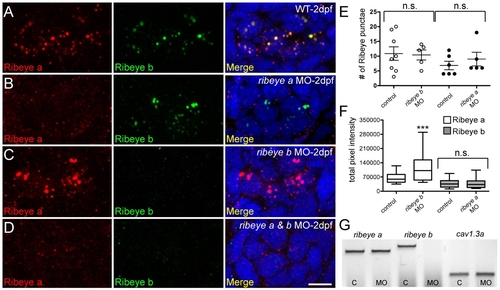
Morpholino-mediated knockdown of ribeye a and ribeye b in 2-day-old zebrafish larvae. (A-D) Representative confocal z-projections of Ribeye a (red) and Ribeye b (green) immunolabel in neuromast hair cells of wild-type (A), ribeye a morphant (B), ribeye b morphant (C), and ribeye a and ribeye b morphant larvae (D). Merged images include DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 3 μm. E) The average number of Ribeye a punctae per neuromast (white circles) in control (11±2) and ribeye b MO-injected (10±2) larvae, and the average number of Ribeye b punctae (black circles) in control (7±1) and ribeye a MO-injected (9±2) larvae. Each circle represents neuromast 1 in the trunk of an individual larva. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (F) Total pixel intensity (A.U.) of Ribeye a immunolabel in control and ribeye b morphants (Mann-Whitney U-test: P<0.0001), and Ribeye b in control and ribeye a morphants (Mann-Whitney U-test: P=0.80). Whiskers indicate the 10th and 90th percentiles. (G) RT-PCR analysis of control (C) and antisense ribeye b splice site MO-injected whole larvae. cav1.3a was used as a control. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Antibodies: | |
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |