Fig. 7
|
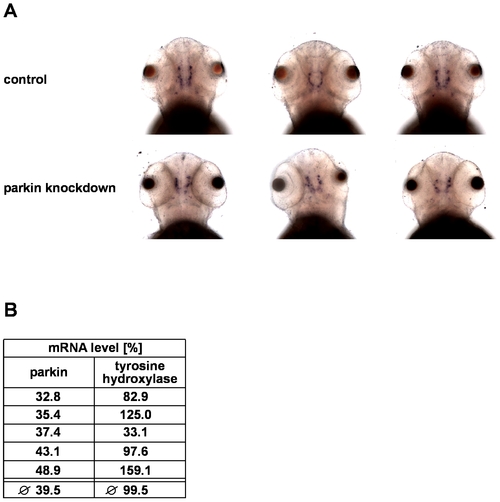
Parkin deficiency has no effect on tyrosine hydroxylase levels in zebrafish. (A) In situ hybridization using an antisense RNA probe for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) as a marker for dopaminergic neurons. Staining of parkin knockdown and control-injected zebrafish larvae shows large interindividual variations in both the control and parkin knockdown group. Dorsal views of three-day-old larvae. (B) There is no correlation between the efficiency of parkin knockdown and TH mRNA levels. TH mRNA levels were quantified in parkin-knockdown zebrafish using semi-quantitative real-time PCR. The amount of zebrafish TH-specific mRNA was normalized to β-actin in parkin GT-grip-injected zebrafish larvae compared to control-injected embryos at day 3 after injection.The graph shows the results of 5 independent experiments. In each experiment 10–15 zebrafish larvae per group were analyzed. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |