Fig. 4
|
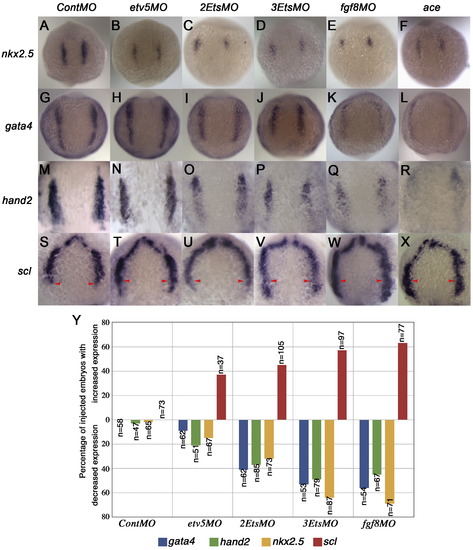
Pea3 ETS factors are required to maintain cardiac progenitors. (A–X) Dorsal views at 10-somite stage. In situ probe listed on left and MO above. (A–D) nkx2.5 expression was reduced as multiple Pea3 factors were knocked down (D). This was similar to fgf8MO knock-down and in ace mutants (E–F). (G–J; M–P) gata4 expression (G–J) and hand2 expression (M–P) were also reduced after Pea3 depletion (J, P). A similar phenotype was observed in fgf8MO knock-downs and in ace mutants (K, L;Q, R). (S–V) Dorsal view of scl expression indicated expansion of endothelial lineages in EtsMO injections (T–V) as indicated by arrowheads that mark the caudal limit in uninjected embryos (S). Similar results were noted in fgf8MO and ace embryos suggesting that FGF signaling is required to maintain cardiac progenitors and to limit endothelial lineages to the rostral ALPM (W, X). (Y) Graph providing quantitative data for MO experiments. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 342(1), Znosko, W.A., Yu, S., Thomas, K., Molina, G.A., Li, C., Tsang, W., Dawid, I.B., Moon, A.M., and Tsang, M., Overlapping functions of Pea3 ETS transcription factors in FGF signaling during zebrafish development, 11-25, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.