Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100616-10
- Publication
- Stewart et al., 2010 - Phosphatase-Dependent and -Independent Functions of Shp2 in Neural Crest Cells Underlie LEOPARD Syndrome Pathogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
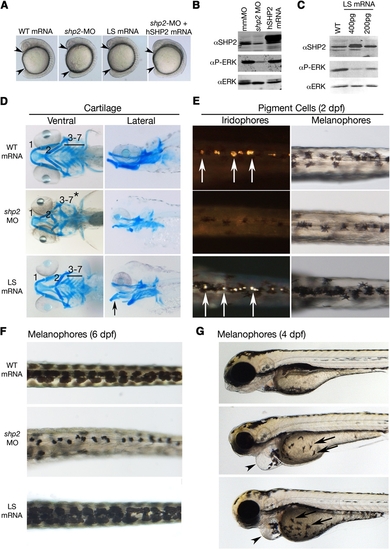
Effects of LEOPARD Syndrome Mutants Are Not Equivalent to shp2 Deficiency (A) Lateral views of 12 somite stage embryos injected with the indicated mRNAs or MOs. Arrowheads indicate distance between the head and tail. (B) Immunoblot showing lysates from embryos injected with the shp2 MO, compared with control (mmMO) or WT human PTPN11 (hSHP2) mRNA. Total Erk is indicated as a loading control. (C) Immunoblot showing dose-dependent dominant-negative effects on pErk levels in embryos injected with LSA462T mRNA compared with uninjected controls (WT). (D) Alcian blue stains of 6 dpf embryos injected with the indicated mRNAs or shp2 MO. Left panels, ventral view; right panels, lateral view. (E) Dorsal views of 2 dpf embryos, in dark (left) and bright (right) field, showing loss of iridophores (white arrows) and melanophores in shp2 MO-injected embryos. LS mRNA injection increases pigment cell numbers. (F) Dorsal views of melanophores at 6 dpf, showing pigment cells in WT mRNA-, MO-, and LS mRNA-injected embryos. (G) Lateral views of 4 dpf embryos. Note delayed migration of melanophores to the yolk in MO- and LS mRNA-injected embryos (black arrows), cardiac edema (arrowheads), and jaw defects. See Figure S1 for additional quantification and data. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | 5-9 somites to Day 6 |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 18(5), Stewart, R.A., Sanda, T., Widlund, H.R., Zhu, S., Swanson, K.D., Hurley, A.D., Bentires-Alj, M., Fisher, D.E., Kontaridis, M.I., Look, A.T., and Neel, B.G., Phosphatase-Dependent and -Independent Functions of Shp2 in Neural Crest Cells Underlie LEOPARD Syndrome Pathogenesis, 750-762, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell