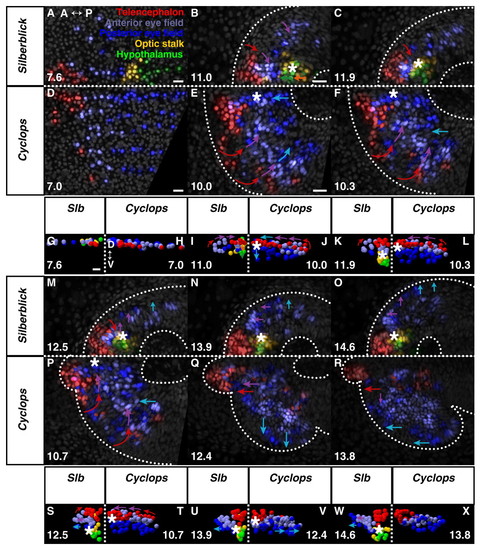
Eye morphogenesis in cyc morphant and slb. (A-F,M-R) Dorsal projections, anterior to left; (G-L,S-X) frontal projections, dorsal up. slb (A,G) and cyc morphant (D,H) forebrain regions prior to neurulation. Anterior limit of keel formation, as with wild-type, begins with hypothalamus in slb (B) but is far anterior within the anterior eye field in cyc morphant (E). (C,F) Keel movement is attenuated in both cyc morphant and slb, relative to wild-type, never emerging anterior to the telencephalon. (I,K) Anterior tissue is displaced progressively deep in slb. (J,L) Medial eye field occupies the ventral midline in cyc morphant. (M-O) Retarded medial eye-field reorganisation and evagination in slb. (S,U,W) Deep keel persists in slb. (P,Q,T,V) Normal medial convergence of telencephalon and anterior eye field in cyc morphant. (R,X) Subducted eye field remains medial within keel after evagination. Square dotted line, midline. Asterisk, anterior tip of neural keel. Arrows indicate the direction of movement of the cells. Time (bottom left- or right-hand corner) in hpf. Colours are indicated in A. See Movies 7 (slb), 8 (cyc morphant), 9 and 10 in the supplementary material. A, anterior; P, posterior; D, dorsal; V, ventral; hpf, hours post fertilisation. Scale bars, 25 μm.
|

