Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080715-17
- Publication
- Krens et al., 2008 - Distinct functions for ERK1 and ERK2 in cell migration processes during zebrafish gastrulation
- Other Figures
- (all 14)
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
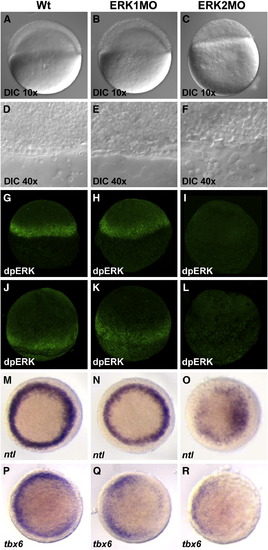
Saturating knockdown of ERK2 prohibits epiboly initiation and revealed ERK2 to be the active MAPK in the margin. Embryos were injected with 0.4 mM ERK1MO (B, E, H, K, N, Q) or ERK2MO (C, F, I, L, O, R) and compared to wild type embryos (A, D, G, J, M, P). Nomarski/differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy using a Zeiss EC Plan-Neofluar 10x/0.30 objective (A, B, C) and a Zeiss Plan-Neofluar 40x/0.75 ∞/0.17 (D, E, F) was used to monitor the margin at the onset of gastrulation (4.5 hpf). Localization of dpERK was detected by immuno-localization in wild type, ERK1MO and ERK2MO injected embryos at 4.5 hpf (G–I) and 8 hpf (J–L) by phospho-specific ERK antibody. Images in panels G–L were taken by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Mesoderm formation was followed using in situ hybridization markers ntl (M–O) and tbx6 (P–R), top view, presumptive dorsal side right. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Dome |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 319(2), Krens, S.F., He, S., Lamers, G.E., Meijer, A.H., Bakkers, J., Schmidt, T., Spaink, H.P., and Snaar-Jagalska, B.E., Distinct functions for ERK1 and ERK2 in cell migration processes during zebrafish gastrulation, 370-383, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.