Fig. 2
|
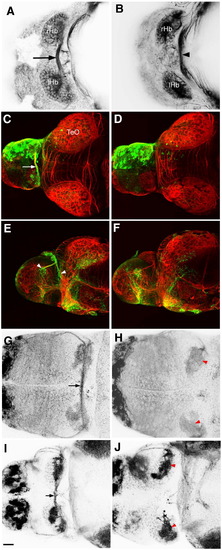
The habenular commissure is absent in esrom mutants. (A) Axon tracts in the dorsal forebrain of 3 dpf wt embryo, visualized with an antibody to acetylated tubulin. The habenular commissure (arrow) is visible between the left and right habenulae. (B) An esrom mutant at 3 dpf. The habenular commissure is absent. The posterior commissure is indicated (arrowhead). (C–F) Unilateral electroporation with eGFP, showing the presence of the habenular commissure (arrow, C) and contralateral terminations (arrowheads, E) in a wild type embryo. These are absent in an esrom mutant (D, F). Habenular afferents can be visualized with an antibody to mGluR2/3 (G, H) or SV2 (I, J). The commissure is visible in wild types (arrow, G, I). In mutants (H, J), axons terminate in the ipsilateral neuropils (red arrowheads). All embryos are shown in dorsal view, except panels E and F which are lateral views. rHb: right habenula; lHb left habenula; TeO: tectum opticum. Scale bar = 20 μm. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Protruding-mouth |
Reprinted from Molecular and cellular neurosciences, 37(2), Hendricks, M., Mathuru, A.S., Wang, H., Silander, O., Kee, M.Z., and Jesuthasan, S., Disruption of Esrom and Ryk identifies the roof plate boundary as an intermediate target for commissure formation, 271-283, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell Neurosci.