Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-070921-3
- Publication
- Gardiner et al., 2007 - A global role for zebrafish klf4 in embryonic erythropoiesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
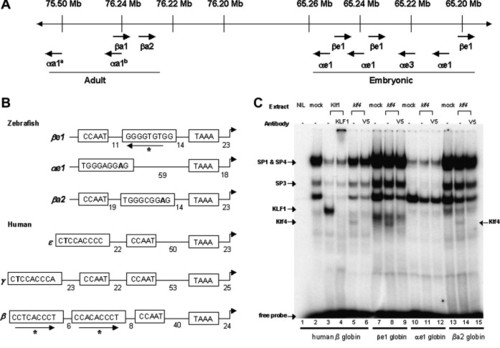
Organisation of CACCC, TATA, and CCAAT box motifs in zebrafish and human globin genes and CACCC box binding by Klf4. (A) Schematic of the organisation of the zebrafish embryonic (e) and adult (a) α and β globin genes on chromosome 3. (B) Organisation of the zebrafish βe1, αe1 and βa1 globin gene promoter elements derived from BX004811. The human &epsilon-, &gamma-, and β-globin gene promoter elements were derived from U01317. The duplicated human γ-globin genes, Gγ and Aγ, have identical promoter sequences. Numbers indicate spacing in base pairs between the TAAA, CACCC and CCAAT box elements. Arrows indicate canonical KLF binding sites. Bases in bold indicate bases which differ from the 9 bp consensus, CCN–CNC–CCN. (C) Electromobility gel shift assay showing both KLF1 and Klf4 bind to the human β globin CACCC site (lanes 3 and 5). In addition, Klf4 binds to the embryonic βe1 globin CACCC site (lane 8) and a non-canonical CACCC site in the βa2 globin promoter (lane 14) indicated by a gel supershift in the presence of a V5 antibody (lanes 9 and 15). Klf4 does not bind the αe1 globin CACCC site (lanes 11 and 12). The motilities of SP1, SP4, and SP3 DNA complexes from COS7 cells were assigned based on previous work using specific antibodies to these. |
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 124(9-10), Gardiner, M.R., Gongora, M.M., Grimmond, S.M., and Perkins, A.C., A global role for zebrafish klf4 in embryonic erythropoiesis, 762-774, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.