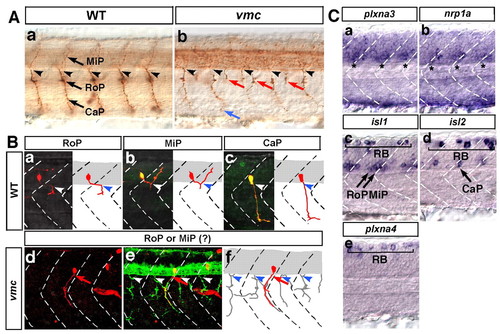
Plxna3 (vmc) is required for correct axonal pathfinding of the primary motoneurons. (A) Axons of primary motoneurons of wild-type (a) and vmc (b) zebrafish embryos at 28 hpf. The blue arrow indicates an axon that showed abnormal pathfinding after extending from the normal exit point. Red arrows indicate axons that extended from the abnormal exit points. (B) Kaede-labelled primary motoneurons of wild-type and vmc Isl1-GFP embryos at 36 hpf (a-f, red). Arrows indicate the axons of RoP- or MiP-like neurons that extended out of the spinal cord through abnormal exit points (d-f). In e, all axons were visualised using a cocktail of znp-1 and zn-1 antibodies (green). Arrowheads in A and B indicate the normal exit points. (C) Expression of plxna3, nrp1a, isl1, isl2 and plxna4 mRNA in the spinal cord at 24 hpf. Asterisks indicate expression of plxna3 (a) and nrp1a (b) mRNA. Bracket (c-e) indicates Rohon-Beard sensory neurons (RB). In all images, dorsal is top, anterior is left. CaP, caudal primary motoneuron; MiP, middle primary motoneuron; RoP, rostral primary motoneuron.
|

