Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-070514-9
- Publication
- Curado et al., 2007 - Conditional targeted cell ablation in zebrafish: A new tool for regeneration studies
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
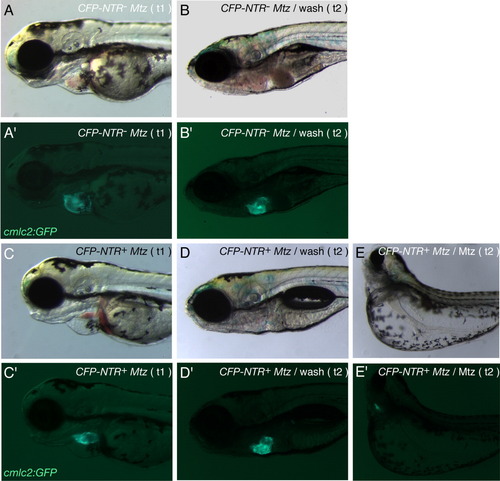
Functional heart tissue recovery after Nitroreductase/Metronidazole (NTR/Mtz) -mediated cell ablation. A-D: Brightfield images of a control Tg(cmlc2:GFP) larva (A,B) and Tg(cmlc2:CFP-NTR)s890; Tg(cmlc2:GFP) larva (C,D) exposed to 10 mM Mtz at 48 hours postfertilization (hpf), after 24 hr incubation in Mtz (t1; A,C) and after 96 hr washing-out in Mtz-free medium (t2; B,D). E: Brightfield image of Tg(cmlc2:CFP-NTR)s890; Tg(cmlc2:GFP) larva incubated in 10 mM Mtz continuously from 48 to 168 hpf (t2). A′,B′,C′,D′,E′: Fluorescence images showing Tg(cmlc2:GFP) expression (green) in the larvae above (A′ corresponding to A, B′ to B, C′ to C, D′ to D, and E′ to E). Tg(cmlc2:CFP-NTR)s890; Tg(cmlc2:GFP) larvae whose heart tissue was severely damaged as a result of exposure to Mtz for 24 hr (C, C′) were able to replace damaged tissue by functional tissue upon removal of the drug: after 96 hr in Mtz-free medium, the larvae showed a morphologically wild-type heart (D′) and no blood pooling (D). Tg(cmlc2:CFP-NTR)s890; Tg(cmlc2:GFP) larvae continuously exposed to Mtz for 120 hr showed enhanced cardiac and body phenotype defects: curved body, large yolk edema, small eyes, enlarged eye pockets (E), and collapsed, nonfunctional heart chambers of significantly reduced size (E′). |