Fig. 5
|
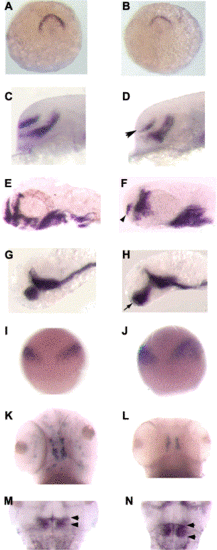
col mutants display regionalized posteriorization within the anterior neuroectoderm. (A,B) anf is expressed along the anterior edge of the neuroectoderm in wild-type embryos (A; dorsal view) at tailbud stage and anf expression is decreased in col mutant embryos (B). (C–F) The telencephalic stripe of dlx2 expression in a lateral view of a (C,D) 24 hpf and (E,F) 40 hpf col mutant (D,F arrowhead) is reduced compared to wild-type (C,E). (G,H) Lateral views of ventral diencephalic expression of shh in 32 hpf wild-type (G) and col mutant (H) embryos illustrates the anterior expansion of shh expression (arrowhead in H) in col mutant embryos. (I,J) At 90% epiboly, wnt8b is expressed at the MHB in wild-type embryos (I). wnt8b expression is expanded in col mutants (J). (K,L) The number of tyrosine hydroxylase-expressing dopaminergic neurons of the midbrain is reduced in col mutant (L) embryos as compared to wild-type (K) embryos at 3 dpf. (M,N) pax2.1 expression at the MHB in 48 hpf wild-type (M) and col mutant (N) embryos. Arrowheads indicate the expanded anterior–posterior extent of pax2.1 expression in col mutant embryos. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 267(1), Nambiar, R.M., and Henion, P.D., Sequential antagonism of early and late Wnt-signaling by zebrafish colgate promotes dorsal and anterior fates, 165-80, Copyright (2004) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.