Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-050830-10
- Publication
- Holzschuh et al., 2005 - Requirements for endoderm and BMP signaling in sensory neurogenesis in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- (all 9)
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
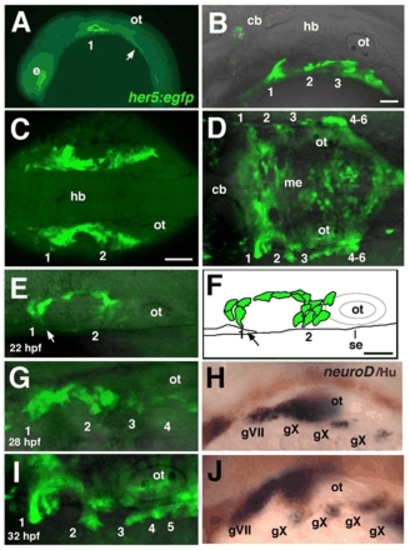
Pharyngeal pouch formation coincides with epibranchial neurogenesis. (A-E,G,I) Confocal images of live, homozygous her5:egfp transgenic embryos; anterior to the left. (A) 16 hpf embryo, lateral view; pouch 1, as well as an unsegmented endoderm located further posteriorly (arrow), is labeled. (B) 26 hpf embryo, lateral view; pouches 1-3 are labeled. (C) 18 hpf embryo, dorsal view; pouches 1 and 2 on each side are joined along the AP axis by a continuous band of endoderm surrounding mesenchyme of the second arch. (D) 32 hpf embryo, dorsal view; pouches (1-6) form only in the most lateral endoderm, while her5:egfp also labels a flattened layer of medial endoderm (me). (E,G,I) Sequence of confocal images of her5:egfp, in dorsal view, at 22 (E), 28 (F) and 32 (H) hpf. (E) 22 hpf embryo; pouch-forming endodermal cells extend filopodial processes laterally (arrow). (F) An illustration of the embryo shown in E. Arrow indicates movement of GFP+ cells toward the surface ectoderm (se). (G-J) Embryos analyzed for her5:egfp expression at 28 (G) and 32 (I) hpf were fixed and subjected to in situ hybridization (H,J) for neurod (blue) combined with immunolabeling with α-Hu antibody (brown). 1-6, pharyngeal pouches; cb, cerebellum; e, eye; gV, trigeminal ganglion; gVII, facial (geniculate) ganglion; gIX, glossopharyngeal (petrosal) ganglion; gX, vagal (nodose) ganglion; hb, hindbrain; me, medial endoderm; ot, otic vesicle. Scale bars: 50 μm; in B for A,B; in C for C,D; in F for E-J. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Prim-15 |