- Title
-
Regulation of neuronal specification in the zebrafish spinal cord by Delta function
- Authors
- Appel, B. and Eisen, J.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
deltaA expression in trunk neural plate and later neural tube. (A) Dorsal view focused on trunk of a 2- to 3-somite-stage embryo, anterior left, hybridized with digoxygenin-labeled antisense deltaA RNA. High levels of expression are revealed in medial (m) and lateral (l) regions of neural plate. (B) Transverse section through trunk of a 3-somite-stage embryo. Expression is specific to neuroepithelium (between asterisks). (C) Transverse section through trunk of a 20-somite-stage embryo. Cells expressing high levels of deltaA message are largely located near the neural tube basal surface (arrows) but are also in apically positioned cells (asterisk). nc, notochord; s, somitic mesoderm. Scale bar, 40 μm (A), 20 μm (B), 10 μm (C). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
deltaA is transiently expressed in cells specified for neuronal fate. Embryos labeled for nuclear Isl protein (brown), revealing pPMNs and pRBs, and deltaA RNA (blue). (A) Dorsal view of medial neural keel, at the position of the third and fourth somites, at the 4-somite stage (11.3 h). Doubly labeled cells (arrows) indicating pPMNs expressing deltaA. Many cells expressing deltaA at high level do not express Isl (white arrowheads). (B) Similar view to A, at the 6- somite stage. pPMNs (asterisks) do not express deltaA and lie ventral to most cells expressing deltaA at high level. (C) Dorsal view of lateral neural plate, at the position of the 2nd and 3rd somites, of a 3-somite-stage embryo. Doubly labeled pRBs are indicated by arrows. (D) Similar view to C of a 6-somite-stage embryo. Most pPMNS (asterisks) no longer express deltaA RNA. A single doubly labeled cell is indicated by the arrow. (E) Saggital section of 24 h spinal cord. Some presumptive secondary motoneurons express deltaA RNA (black arrows) while others do not (asterisks). RBs (white arrows) do not express deltaA at this stage. Scale bar, 25 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Delta function regulates neurogenesis. Dorsal views (anterior left) of 6-somite-stage embryos injected with mRNA at early blastula stages and probed for huC expression. In each case, b-galactosidase activity, as lineage tracer, is revealed as light blue staining and huC expression as dark blue. (A) Embryo injected with nlacZ mRNA only. huC is expressed in discontinuous, bilateral rows of cells in medial (m) and lateral (l) regions of neural keel. (B) Embryo injected with full-length deltaA and nlacZ mRNAs. Lineage tracer is distributed thoughout the embryo, with the right side (upper portion) receiving more than the left (lower). huC expression is absent from both lateral domains and the number of huC-expressing cells in the medial rows is reduced, particularly on the right side. Lateral domains seem more sensitive than medial domains to increased deltaA expression (two independent experiments: 40% and 47% of embryos with decreased medial huC expression while greater than 90% of embryos show reduced lateral huC expression). (C) Embryo co-injected with nlacZ and X-Delta-1STU mRNA. Lineage tracer shows that the right side (asterisk) received most of the injected mRNA. The density of huC-labeled neurons is increased in medial and lateral regions of neural keel receiving injected mRNA. Scale bar, 50 μm. |
|
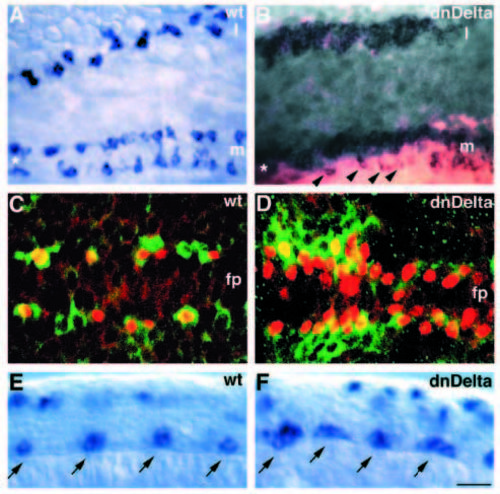
Disruption of Delta function causes overproduction of primary motoneurons. (A) Dorsal view of neural plate of an uninjected 4-somite-stage embryo showing islet1 expression by in situ RNA hybridization in medial (m) and lateral (l) regions. islet1 expression marks pPMNs medially (two longitudinal rows bordering the floorplate, marked by an asterisk) and pRBs laterally. (B) Dorsal view of 4-somite-stage embryo injected with X-Delta-1STU and lacZ mRNA and probed for islet1 expression. Excess pPMNs and pRBs develop medially and laterally, respectively, on the side receiving most injected mRNA. Arrowheads indicate distribution of motoneurons, which is similar to that of uninjected embryos, on the side receiving little mRNA. Asterisk marks position of floorplate between motoneuron rows. (C) Confocal image, dorsal view, of uninjected 6-somite-stage embryo labeled with α-Isl (red) and a-Hu (green) antibodies. α-Isl reactivity precedes that of α-Hu (data not shown); thus, α-Isl+ motoneurons flanking the floorplate (fp) are sometimes unlabeled by α-Hu. Several non-motoneurons (a-Hupositive, α-Isl-negative) are interspersed among motoneurons. (D) Confocal image, dorsal view, of 6-somite-stage embryo injected with X-Delta-1STU mRNA and labeled with α-Isl (red) and α-Hu (green). Nearly every cell flanking the floorplate is a motoneuron. Some motoneurons also develop just dorsal to the floorplate. (E) Wild-type expression pattern of islet2 RNA at 16-somite-stage, shown in lateral view. islet2 is expressed in CaP and VaP motoneurons (arrows). Labeled cells in dorsal spinal cord are pRBs. (F) Similarly staged embryo injected with X-Delta-1STU mRNA and probed for islet2 expression. islet2 is expressed in clusters of cells located at the normal positions of CaP and VaP motoneurons (arrows). Scale bar, 20 μm (A,B), 10 μm (C,D) and 15 μm (E,F). |
|
Disruption of lateral inhibition reduces the number of secondary motoneurons. (A) Lateral view of a 36 h control embryo labeled with zn5, which identifies secondary motoneurons (brackets) and ventral nerves (arrows) exiting the spinal cord. (B) Similar view of a 36 h embryo injected with X-Delta-1STU and nlacZ mRNAs. Lineage tracer (blue staining) is expressed in small clusters of spinal cord cells. Outside the clusters, zn5 labeling looks essentially normal. Cells within lineage-marked clusters are largely zn5-negative, showing that secondary motoneurons have not differentiated. Ventral nerves (arrows) appear reduced in size, suggesting the presence of fewer motor axons than in normal embryos. Scale bar, 20 μM. |
|
Ventral interneurons are reduced in the absence of lateral inhibition. (A) Lateral view of 24 h spinal cord showing distribution of GABA-positive neurons. KA interneurons (arrows) differentiate in ventral spinal cord, VeLD interneurons (arrowheads) are slightly more dorsal and CoSA interneurons (asterisks) are dorsal to VeLDs and just ventral to RBs. (B) Lateral view of a 24 h embryo injected with X-Delta-1STU and nlacZ mRNAs and labeled with anti-GABA. A single VeLD and two CoSA interneurons have differentiated. Scale bar, 10 μm. |