- Title
-
Estrogenic regulation of claudin 5 and tight junction protein 1 gene expression in zebrafish: A role on blood-brain barrier?
- Authors
- Pellegrini, E., Fernezelian, D., Malleret, C., Gueguen, M.M., Patche-Firmin, J., Rastegar, S., Meilhac, O., Diotel, N.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Comp. Neurol.
|
Claudin 5 and tight junction protein 1 gene expression during zebrafish development and in the brain of adult zebrafish. (a–d) Transcript quantification of cldn5a, cldn5b, tjp1a, and tjp1b1 during zebrafish development between zygote stage (1-cell) to 120 h postfertilization (120 hpf or larval day 5). (e–f) Transcript quantification of cldn5a, cldn5b, tjp1a, and tjp1b1 in the whole adult mixed (male + female) zebrafish brain and telencephalon. Note that these data were obtained from the reanalysis of an RNA seq data set generated by Gourain et al. (2021), Rodriguez Viales et al. (2015), White et al. (2017), and Wong & Godwin (2015). FPKM, fragments per kilobase million; RPKM, reads per kilobase million. ****p < .0001. |
|
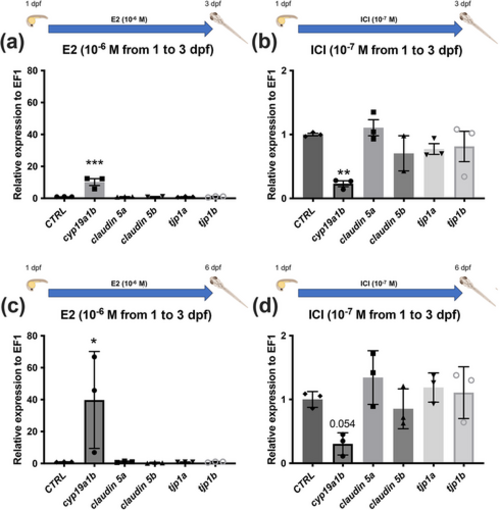
Estrogen signaling has no impact on claudin 5 and tight junction protein 1 gene expression during zebrafish development. (a, b) cldn5 and tjp1 gene expression following treatment with 10−6 M of E2 and with 10−7 M of ICI from 1 to 3 dpf. (c, d) cldn5 and tjp1 |
|
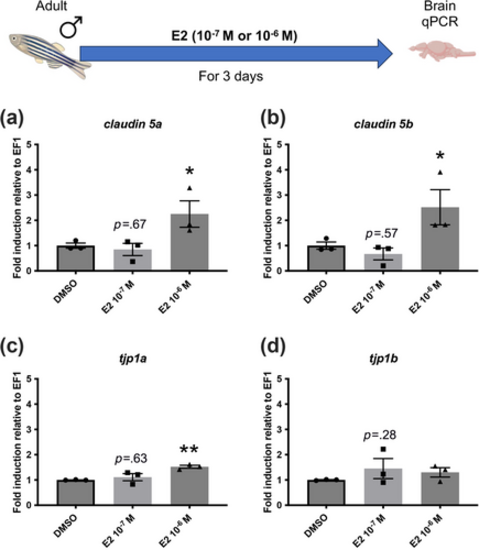
High estrogen concentration increases cldn5 and tjp1 gene expression in the whole adult male brain. (a–d) cldn5 and tjp1 cerebral genes expression following 3 days of treatment with 10−7 and 10−6 M of E2 compared to controls (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]). n |
|
Estrogen modulates tight junction protein 1a and 1b gene expression in the telencephalon of adult zebrafish. (a) cldn5 and tjp1 telencephalic gene expression in adult males following 4 days of treatment with 10−7 |
|
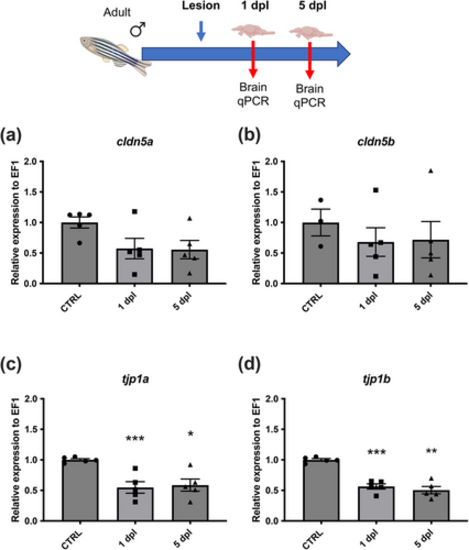
Brain injury decreases claudin and tight junction protein gene expression in males. (a, b) cldn5a and cldn5b gene expressions are not significantly decreased 1 and 5 days after telencephalic brain injury. (c, d) tjp1a and tjp1b |
|
Estradiol treatment after brain injury tends to increase claudin and tight junction protein gene expression compared to untreated controls. (a–d) Zebrafish males treated with 10−7 M of E2 8 h postinjury (hpi) show an increasing trend in blood–brain barrier (BBB) gene expression 1 day after the lesion (dpi). SW, stab-wounded telencephalon. n = 5 pools of three injured telencephalons. |
|
Nuclear estrogen receptors esr1 and esr2a are expressed in endothelial cells. Fluorescent in situ hybridization showing esr1 (a), esr2b (b), and esr2a (c) in red with DAPI counterstaining. Note that arrows point to endothelial cells characterized by their flat and elongated cell nuclei bordering the blood vessels demonstrating expression of esr1 and esr2a in endothelial cells and no esr2b expression. Scale bar: 15 μm. |
|
Estradiol treatment after brain injury reduces blood–brain barrier (BBB) leakage. Zebrafish males treated with 10−7 M of E2 after telencephalic injury show a significant decrease in Evans blue extravasation and consequently a decreased BBB leakage 1 day after the lesion compared to untreated fish. n = 6-7 brains (six controls and seven treated with estradiol). *p < .05. |
|
Aromatase B-positive radial glial cells strongly interact with endothelial cells being able to take up high-density lipoproteins (HDLs). (a–c) Aromatase B immunohistochemistry (red) in Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 fish in which endothelial cells express GFP (green) showing strong interactions between neural stem cells and blood vessels in the ventral nucleus of the ventral telencephalon (Vv) and the dorsomedial region (Dm) of the telencephalon. (d–g) Intraperitoneal injection of HDLs in zebrafish allowed HDL uptake by cerebral endothelial cells as revealed by ApoA1 immunohistochemistry (red) in Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 fish (green) as shown in these transversal sections of two cerebral blood vessels. (h) Intraperitoneal injection of HDLs in Tg(cyp19a1b:GFP) showing ApoA1 (red) proximity with AroB-positive neural stem cell endfeets along a sagittal blood vessel section in the telencephalon. Tg(cyp19a1b:GFP) zebrafish expressed GFP in radial glial cells (RGCs) (Tong et al., 2009). Scale bar: 21 μm (a–b), 14 μm (c–g), and 3.5 μm (h). |
|
Impact of male and female high-density lipoprotein (HDL) injection in claudin and tight junction protein gene expression in adult male brain. (a) Male HDL injection does not change cldn5a, cldn5b, tjp1a, and tjp1b |