- Title
-
Mitochondrial proteins encoded by the 22q11.2 neurodevelopmental locus regulate neural stem and progenitor cell proliferation
- Authors
- Campbell, P.D., Lee, I., Thyme, S., Granato, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Mol. Psychiatry
|
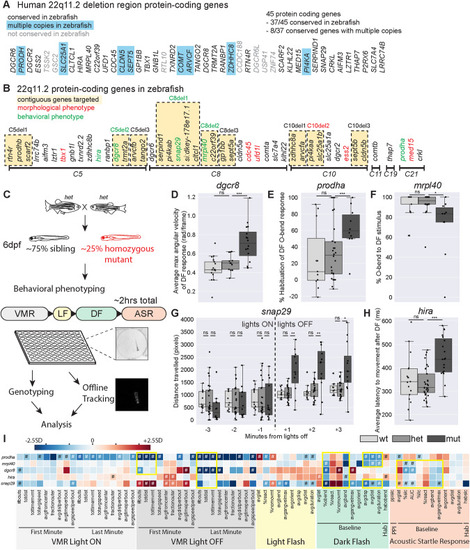
Mutants in five genes including two encoding mitochondrial proteins, display partially overlapping behavioral phenotypes. |
|
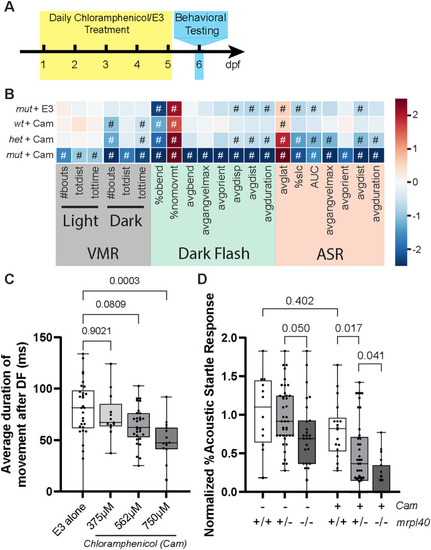
Pharmacologic inhibition of mitochondrial function phenocopies the |
|
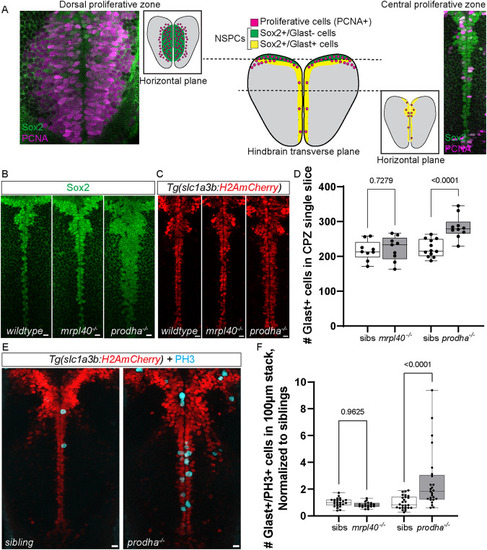
Mitochondrial disruption leads to alterations in brain volume. |
|
|
|
|
|
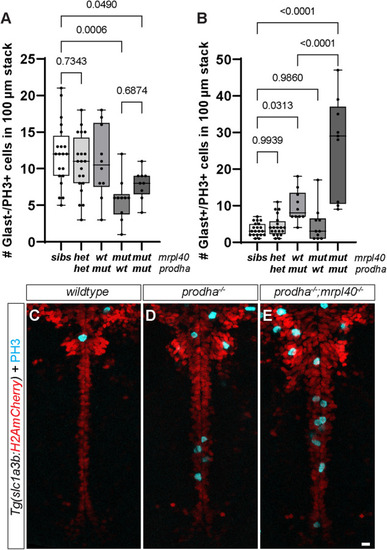
Number of Glast−/PH3+ ( |