- Title
-
Biallelic DAW1 variants cause a motile ciliopathy characterized by laterality defects and subtle ciliary beating abnormalities
- Authors
- Leslie, J.S., Hjeij, R., Vivante, A., Bearce, E.A., Dyer, L., Wang, J., Rawlins, L., Kennedy, J., Ubeyratna, N., Fasham, J., Irons, Z.H., Craig, S.B., Koenig, J., George, S., Pode-Shakked, B., Bolkier, Y., Barel, O., Mane, S., Frederiksen, K.K., Wenger, O., Scott, E., Cross, H.E., Lorentzen, E., Norris, D.P., Anikster, Y., Omran, H., Grimes, D.T., Crosby, A.H., Baple, E.L.
- Source
- Full text @ Genet. Med.
|
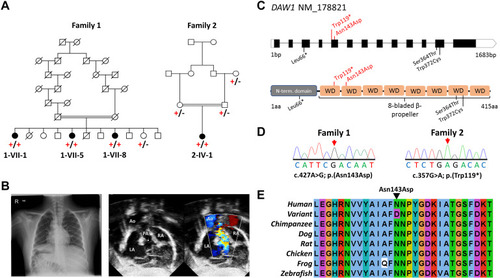
Figure 1. DAW1 variants, family pedigrees, and clinical images. A. Simplified pedigree of the extended Mennonite family (family 1) and the Palestinian family (family 2) in which segregation of the [NM_178821.2:c.427A>G; p.(Asn143Asp)] and [NM_178821.2: c.357G>A; p.(Trp119∗)] DAW1 variants are indicated (+, variant; –, wild type). B. Chest radiograph from individual 2-IV-1 from family 2 showing the right sided aortic arch, right sided stomach, and situs inversus. Echocardiogram imaging from the same individual showing atrial situs inversus. C. Schematic showing DAW1 intron–exon genomic organization (upper panel) and polypeptide domain architecture (lower panel), with position of DAW1 variants indicated. Variants identified in this study are indicated above the schematic in red, variants identified in previous studies are indicated below the schematic in black. D. Sequencing electropherograms from individuals homozygous for the p.(Asn143Asp) and p.(Trp119∗) variants. E. Multiple sequence alignment of the Mennonite DAW1 NM_178821.2:c.427A>G p.(Asn143Asp) variant; the substituted residue is indicated by the black arrow. Ao, aorta; LA, left atrium; PA, pulmonic artery; RA, right atrium. |
|
Figure 2. In vivo modeling of DAW1 variants using zebrafish mutant. A. Schematic of zebrafish Daw1 protein showing the location of the 2 amino acid deletion present in daw1b1403 mutants. B. Quantitation of cardiac looping phenotypes with representative images in daw1b1403 mutants (n = 54) and sibling controls (n = 118). Scale bar: 50 μm. C. Quantitation of dand5 expression with representative images in daw1b1403 mutants (n = 30) and sibling controls (n = 30). Scale bars: 50 μm. Di. Quantitation of the area occupied by motile cilia in KV at the 10-somite stage. Each data point represents a distinct embryo. Dii. Representative temporal image correlation spectroscopy images of KV cilia motility where white/gray pixels show regions of periodic motion. Scale bars: 5 μm. E. Dot plot showing the percentage of daw1b1403 mutant embryos exhibiting abnormal cardiac looping laterality after injections with mRNA encoding either wild-type or variant Daw1. ∗P < .05; ∗∗∗∗P < .001; ns, not significant; unpaired t test was applied. F. Summary table of zebrafish rescue assay data. KV, Kupffer’s vesicle; mRNA, messenger RNA; ns, not significant; sib, sibling control. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
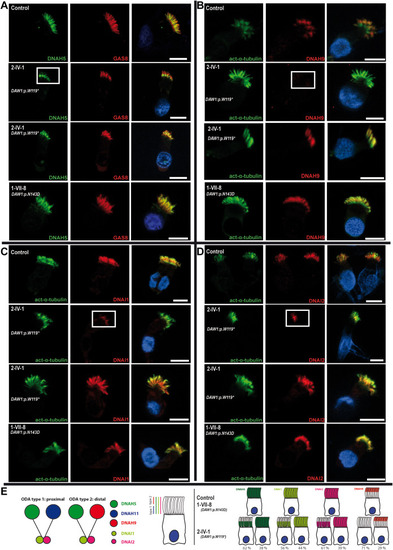
Figure 3. DAW1 loss-of-function variants cause a variable partial defect in the assembly of the outer dynein arm components DNAH5, DNAH9, DNAI1, and DNAI2 to the ciliary axonemes. A-D. Respiratory epithelial cells derived from the affected Palestinian child (2-IV-1) homozygous for DAW1 NM_178821.2: c.357G>A; p.(Trp119∗), a Mennonite individual (1-VII-8) homozygous for DAW1 variant NM_178821.2:c.427A>G; p.(Asn143Asp) and an unrelated control. Cells were double-labeled with antibodies directed against DNAH5 (green, A), GAS8 (red, A), DNAH9 (red, B), DNAI1 (red, C), DNAI2 (red, D), and acetylated alpha-tubulin (green, B, C, and D). Nuclei were stained using Hoechst 33342 (blue). In an unaffected control and affected individual 1-VII-8, DNAH5, DNAI1, and DNAI2 localized to the whole axonemal length and DNAH9 localized to the distal compartment of the axonemes. However, in affected individual 2-IV-1, DNAH5, DNAI1, and DNAI2 only localized to the proximal part of the ciliary axonemes in a proportion of the analyzed cells; 62%, 56%, and 61%, respectively, and DNAH9 was absent in 71% of the cells (white box), indicating that recessive loss-of-function variants in DAW1 variably affect the distal localization of ODA proteins. Scale bars: 10 μm. E. (Left side) Schematic showing the 2 types of ODAs in human: ODA type 1 localized to the proximal part of the cilia and contains DNAH5 and DNAH11 and ODA type 2 localized to the distal part of the cilia and contains DNAH5 and DNAH9. Both types contain the intermediate chains DNAI1 and DNAI2. (Right side) Schematic highlights the distal loss of DNAH5, DNAI1, DNAI2, and DNAH9 from the ciliary axonemes of affected individual 2-IV:1 with the corresponding percentages. ODA, outer dynein arm. |