- Title
-
Irf2bp2a regulates liver development via stabilizing P53 protein in zebrafish
- Authors
- Yan, L., Gao, S., Zhu, J., Zhou, J.
- Source
- Full text @ BBA General Subjects
|
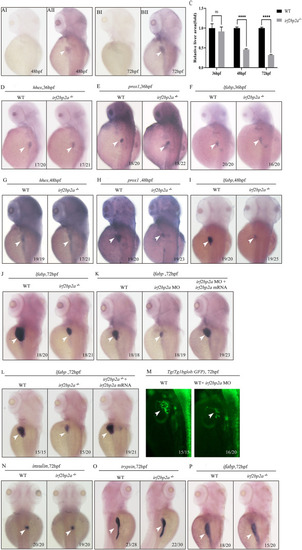
Fig. 1. Deficiency of zebrafish irf2bp2a led to a reduction of liver size. (A, B) WISH analysis of irf2bp2a expression in zebrafish embryos at 48 hpf and 72 hpf (AII, BII). Embryos incubated with irf2bp2a sense probe are shown as negative controls (AI, BI). (C) The relative liver area measured. The result shown is fold difference compared with the level detected in control embryos. p values are denoted by asterisks. (Student t-test, N ≥ 3. Error bars represent mean ± SD, ns, not significant,****P < 0.0001). (Dsingle bondI) WISH assay of hhex (D, G), prox1 (E, H) and lfabp (F, I) at 36 hpf and 48 hpf, respectively. (M) irf2bp2a MO injection in Tg(Tp1bglob:GFP) line which marks the intrahepatic biliary cells. (J, Nsingle bondP) WISH analysis of lfabp (J), insulin (N), trypsin (O) and ifabp (P) at 72 hpf. (K,L) Irf2bp2a mRNA rescue assays in irf2bp2a−/− embryos and morphant embryos at 72 hpf. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
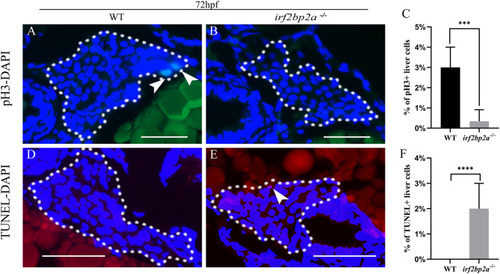
Fig. 2. Deficiency of irf2bp2a leads to decreased proliferation and enhanced apoptosis of liver cells. (A, B, D, E) The proliferation and apoptosis status of hepatic cells were detected by pH3 staining and TUNEL assay in 72 hpf embryos. The sections were counterstained with DAPI to label the nucleus. White dashed lines indicate the liver boundary. White arrows indicate pH3 or TUNEL positive cells. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C, F) Statistical analysis of hepatocyte proliferation and apoptosis. p values are denoted by asterisks. (Student t-test, N ≥ 3. Error bars represent mean ± SD, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
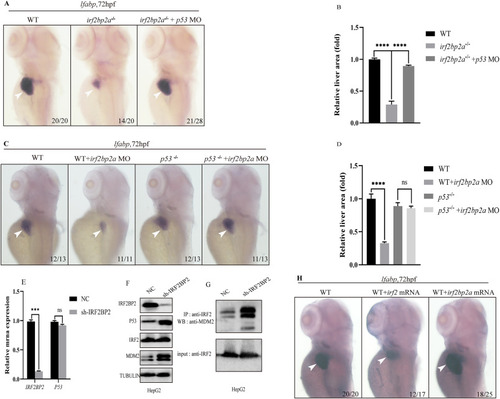
Fig. 3. In the absence of Irf2bp2a, p53 pathway is aberrantly activated due to impaired turnover, which contributes to the defective liver development. (A) WISH assay of lfabp at 72 hpf in irf2bp2a−/− embryos, and irf2bp2a−/− embryos injected with p53 MO. (C) WISH assay of lfabp in WT, WT embryos injected with irf2bp2a MO, p53−/−, and p53−/− embryos injected with irf2bp2a MO. (B, D) The relative liver area measured. The data shown is fold difference compared with the level detected in control embryos. p values are denoted by asterisks. (Student t-test, N ≥ 3. Error bars represent mean ± SD, ns, not significant, ****P < 0.0001). (E) IRF2BP2 and P53 mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR in HepG2 cells after transfection of an irrelevant shRNA (NC, non-specific control) or a shRNA against IRF2BP2 (sh-IRF2BP2). (Student t-test, N ≥ 3. Error bars represent mean ± SD, ns, not significant, ***P < 0.001). (F) Western blot analysis of IRF2BP2, P53, IRF2 and MDM2 in WT and IRF2BP2-knockdown HepG2 cells. (G) IRF2 protein was immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-IRF2 antibody in WT and IRF2BP2-knockdown HepG2 cells, then MDM2 protein was detected by western blot analysis. (H) WISH assay of lfabp in WT, WT embryos injected with full length irf2 or irf2bp2a mRNA. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
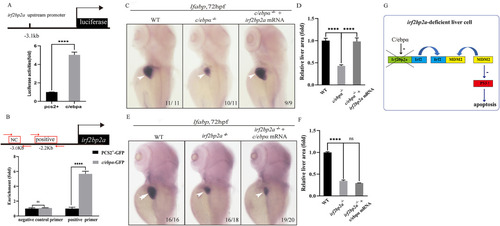
Fig. 4. C/ebpα is epistatic to irf2bp2a in liver development. (A) Luciferase reporter assay. Bars showed the relative luciferase activity on the zebrafish irf2bp2a promoter (−3.1 kb) (Student t-test, N ≥ 3. Error bars represent mean ± SD,****P < 0.0001). (B) CHIP-PCR assay in zebrafish larvae expressing GFP or GFP-C/ebpα using an anti-GFP antibody. The irf2bp2a promoter region could be specifically co-immunoprecipitated with GFP-C/ebpα. (Student t-test, N ≥ 3. Error bars represent mean ± SD,****P < 0.0001). (C) WISH assay of lfabp in WT, c/ebpα−/− embryos and c/ebpα−/− embryos injected with irf2bp2a mRNA. (E) WISH assay of lfabp in WT, irf2bp2a−/− embryos and irf2bp2a−/− embryos injected with c/ebpα mRNA. (D, F) The relative liver area measured. The result shown is fold difference compared with the level detected in control embryos (Student t-test, N ≥ 3. Error bars represent mean ± SD, ns, not significant, ****P < 0.0001). (G) Model of irf2bp2a regulatory network in liver development. A C/ebpα-Irf2bp2a-P53 axis controls liver development in zebrafish. As a downstream target of C/ebpα, Irf2bp2a can compete with Mdm2 to recruit Irf2, which in turn affects the stability of P53 protein. PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Biochimica et biophysica acta. General subjects, 1866(10), Yan, L., Gao, S., Zhu, J., Zhou, J., Irf2bp2a regulates liver development via stabilizing P53 protein in zebrafish, 130186, Copyright (2022) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ BBA General Subjects