- Title
-
Zebrafish: An In Vivo Screening Model to Study Ocular Phenotypes
- Authors
- Quint, W.H., Tadema, K.C.D., Crins, J.H.C., Kokke, N.C.C.J., Meester-Smoor, M.A., Willemsen, R., Klaver, C.C.W., Iglesias, A.I.
- Source
- Full text @ Transl Vis Sci Technol

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |
|
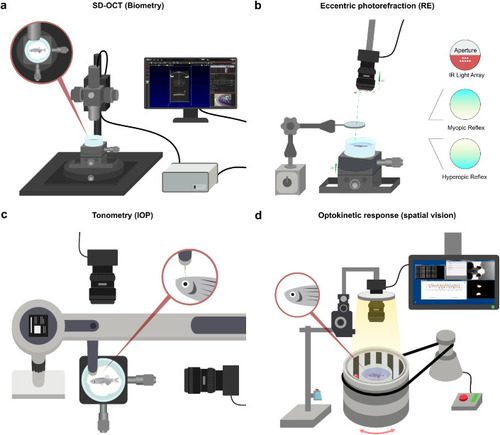
Human ophthalmic assays can be applied in zebrafish to measure ocular performance. Schematic overview of the pipeline of assays used to screen for ocular phenotypes in zebrafish. (a) SD-OCT to assess ocular biometry. (b) Eccentric photorefraction to measure refractive error. (c) Rebound tonometry to measure IOP. (d) The OKR to study visual capability. For full protocols see |
|
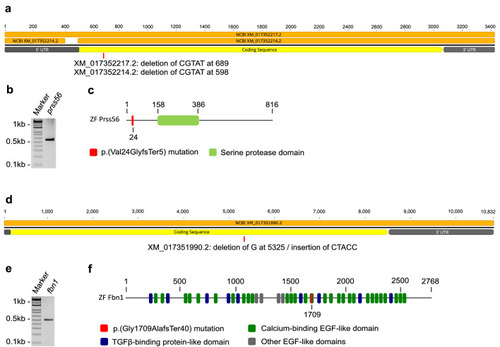
Expression of |
|
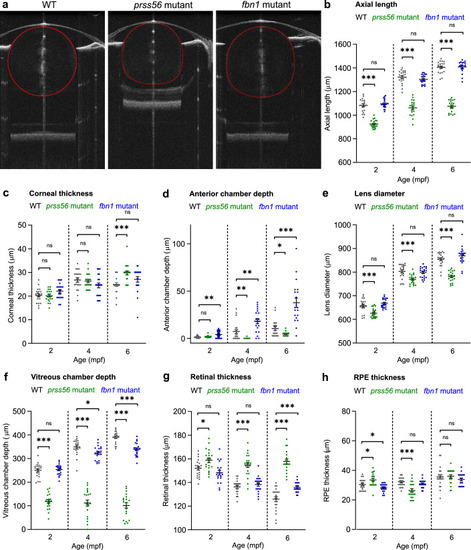
Loss of PHENOTYPE:
|
|
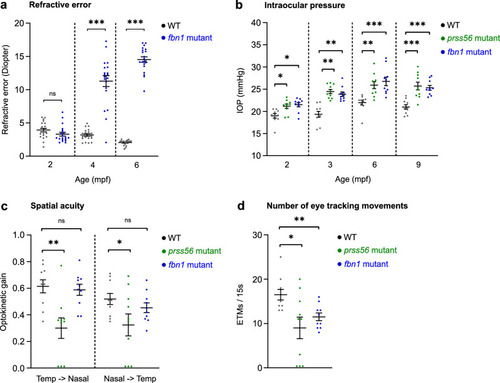
PHENOTYPE:
|