- Title
-
NS398 as a potential drug for autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease: Analysis using bioinformatics, and zebrafish and mouse models
- Authors
- Chen, S., Huang, L., Zhou, S., Zhang, Q., Ruan, M., Fu, L., Yang, B., Xu, D., Mei, C., Mao, Z.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Cell. Mol. Med.
|
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) identified in the GSE7869 and GSE53757 datasets. (A) Volcano maps of DEGs in GSE7869 and GSE53757. (B) Venn diagrams displaying the commonly up‐regulated and down‐regulated DEGs. (C) Protein–protein interaction network of common DEGs. (D) Heatmap of up‐regulated and down‐regulated DEGs. The coloured bars on the top (shades of green) indicate the sample types. (E) GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of common DEGs. (F) Kaplan‐Meier survival analysis of the top 6 unique DEGs in ccRCC ranked by hazard ratio based on the TCGA Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer data (the red line represents high‐expression group, whereas the blue line represents low‐expression group) |
|
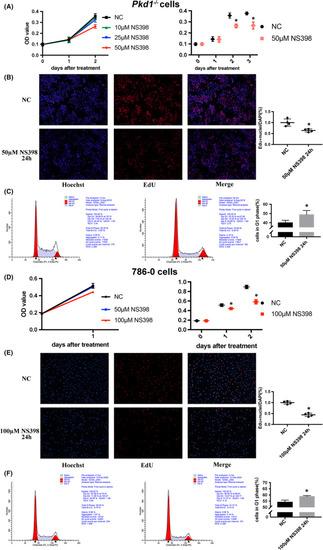
NS398 inhibits |
|
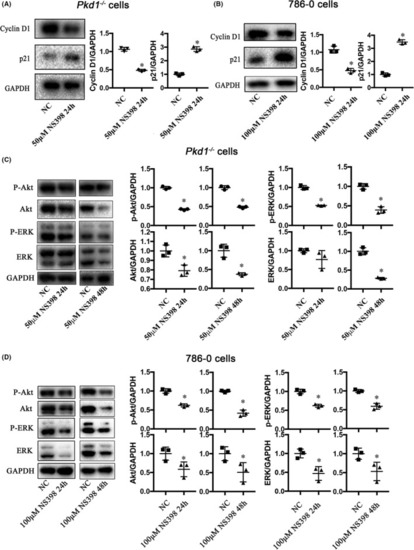
NS398 down‐regulates the abundance of cell cycle and proliferation‐related signalling proteins. (A) and (B) Western blot showing the effects of NS398 on the levels of cyclin D1 and p21 in |
|
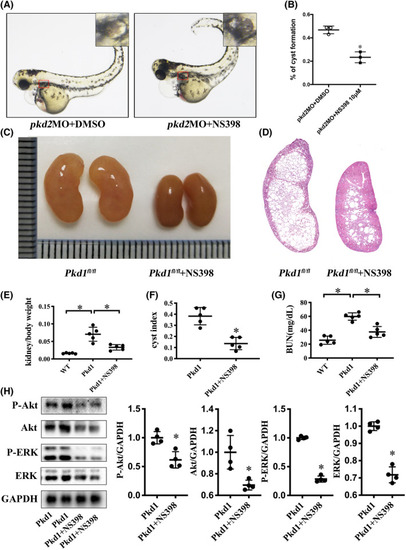
NS398 reduces cyst formation PHENOTYPE:
|