- Title
-
Early life stage transient aristolochic acid exposure induces behavioral hyperactivity but not nephrotoxicity in larval zebrafish
- Authors
- Chen, J., Kong, A., Shelton, D., Dong, H., Li, J., Zhao, F., Bai, C., Huang, K., Mo, W., Chen, S., Xu, H., Tanguay, R.L., Dong, Q.
- Source
- Full text @ Aquat. Toxicol.
|
Effect of AA on malformation and mortality in zebrafish after embryonic exposure from 8–120 hpf. (A) A schematic diagram showing AA chemical structure and the exposure scenario. (B) Incidence of malformation and mortality at 120 hpf (n = 3; each replicate has 20 embryos). Values are plotted as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 indicates significant difference from the vehicle control (0.1 % DMSO). (C) Representative images of larvae at 120 hpf from 0, 4 and 8 μM treated groups. E: eye; CF: craniofacial; SB: swim bladder; USB: uninflated swim bladder; RE: renal edema. |
|
Continuous AA exposure (8–108 hpf) affected larval motor behaviors. (A) A schematic diagram showing zebrafish embryos exposed to 0, 1, 2, and 4 μM AA from 8–108 hpf and sampled at various time points for different motor behavior. (B) Touch response of dechorionated embryos at 36 hpf (n = 24). (C, D) Locomotor response at 72 hpf (C) and 120 hpf (D). Black and white bars at the x-axis represent dark and light conditions, respectively. Dots are the mean activity (72 hpf) or speed (120 hpf) in 60 s intervals, and bars are mean activity or speed (mm/s) in 5-min intervals for each light condition (light or dark) (n = 24). Values are plotted as mean + SD. *P < 0.05 indicates significant differences from the vehicle control. |
|
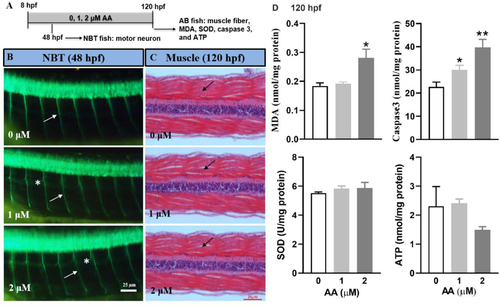
Continuous AA exposure (8–120 hpf) affected axonal growth, induced oxidative stress, and cell apoptosis, but had no effect on muscle fiber. (A) A schematic diagram showing zebrafish embryos exposed to 0, 1, and 2 μM AA from 8–120 hpf and sampled at various time for different endpoints. (B) Representative images showing axonal growth (white arrows) in the primary motor neuron in Tg (NBT: MAPT-GFP) fish at 48 hpf. Asterisks indicate axons with extra proliferated branches. (C) Representative histological sections of muscle fibers (black arrows) from wild type AB line fish at 120 hpf. (D) Oxidative stress measured by MDA, SOD and ATP and cell apoptosis measured by Caspase 3 in wild type AB line fish at 120 hpf. Values are plotted as mean + SD (n = 3; each replicate consists of tissue samples pooled from 20 larvae). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 indicate significant differences from the vehicle control. |
|
Window-specific AA exposure resulted in differential morphological responses. (A) Heatmaps showing the mean incidence (n = 3; each replicate has 20 embryos) of malformation (120 hpf) and mortality (120 hpf) after embryos exposed to 0, 2, 4, 8, and 16 μM AA from 8–120 hpf (I), 8–24 hpf (II), 24–48 hpf (III), and 48–72 hpf (IV). (B) Representative images showing larval eye size (area within dotted circles) at 120 hpf after exposed to 0, 4, and 16 μM AA from 8–24 hpf and 48–72 hpf. (C) The ratio of larval eye size (area) to body length at 120 hpf after exposed to 0, 2, 4, 8, and 16 μM AA from 8–24 hpf (n = 14–16) and 48–72 hpf (n = 12). Values are plotted as mean + SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 indicate significant differences from the vehicle control. |
|
Window-specific AA exposure resulted in differential behavioral responses. (A) A schematic diagram showing zebrafish embryos exposed to 0, 1, 4 and 16 μM AA from 8–24 hpf, or 1 and 4 μM from 48–72 hpf, and sampled at various time points for different motor behavior tests. (B) Spontaneous movement (tail bends/min) of embryos from 19 hpf to 25 hpf (n = 40). (C) Touch response of dechorionated embryos at 36 hpf (n = 24). (D, E) Locomotor response at 72 hpf (D) and 120 hpf (E). Black and white bars at the x-axis represent dark and light conditions, respectively. Dots are the mean activity (72 hpf) or speed (120 hpf) in 60 s intervals, and bars are mean activity or speed (mm/s) in 5-min intervals for each light condition (light or dark) (n = 24). Values are plotted as mean + SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 indicate significant differences from the vehicle control. |
|
Window-specific AA exposure (8–24 hpf) induced aberrant axonal growth, cell apoptosis, and oxidative stress, but had no effect on muscle fiber. (A) A schematic diagram showing zebrafish embryos exposed to 0, 1, and 16 μM AA from 8–24 hpf and sampled at various time for different endpoints. (B) Representative images showing axonal growth (white arrows) in the primary motor neuron in Tg (NBT: MAPT-GFP) fish at 48 hpf. Asterisks indicate axons with extra proliferated branches. (C) Representative histological sections of muscle fibers (white arrows) from wild type AB line fish at 120 hpf. (D) Representative images showing apoptotic cells in the eye region measured by acridine orange (AO) staining at 24 hpf. (E) Quantitative analysis of AO positive cells in (D) (n = 16–24). (F) Cell apoptosis measured by Caspase 3 in wild type AB line fish at 120 hpf. (G-I) Oxidative stress measured by MDA (G), SOD (H) and ATP (I) in wild type AB line fish at 120 hpf. For F-I, n = 3 with each replicate consists of tissue samples pooled from 20 larvae. Values are plotted as mean + SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 indicate significant differences from the vehicle control. |
|
Window-specific AA exposure (8–24 hpf) induced transcriptional changes in genes related to vision and motor neuron development. (A) A schematic diagram showing zebrafish embryos exposed to 0, 1, and 16 μM AA from 8–24 hpf and sampled at 24 hpf and 120 hpf for gene expression analysis. (B-E) Gene expression fold change measured by qPCR (B, D) (n = 3, each replicate consists of tissue samples pooled from 40 larvae) and spatial visualization of rgr, rho, opn1sw1 by in situ hybridization (C, E) for embryos at 24 hpf and 120 hpf. rgr: retinal G protein coupled receptor; crx: cone-rod homeobox protein; rho: rhodopsin, also known as visual purple; opn1sw1: opsin 1 (cone pigments), short-wave-sensitive 1; opn1sw2: opsin 1 (cone pigments) short-wave-sensitive 2; nog: noggin; hox: homeobox gene. Values are plotted as mean + SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 indicate significant differences from the vehicle control (0.1 % DMSO). Arrows in (C, E) indicate gene expression position in the eye region. |