- Title
-
Developmental Neurotoxicity of Environmentally Relevant Pharmaceuticals and Mixtures Thereof in a Zebrafish Embryo Behavioural Test
- Authors
- Atzei, A., Jense, I., Zwart, E.P., Legradi, J., Venhuis, B.J., van der Ven, L.T.M., Heusinkveld, H.J., Hessel, E.V.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health
|
(A) A plot overview showing the entire light-dark transition test applied for the CBZ experiment, after 0–120-hpf exposure. The blue horizontal bar indicates the acclimatization period, while the grey and black bars represent the light and dark period, respectively. The X-axis shows the whole experiment time, whereas the Y-axis shows the time (s) spent in activity within 1 min by the zebrafish embryos (n = 12). Each dot shows the average time (s) spent in activity by 12 embryos/concentration in 1 min of recording, whereas different colours represent different concentrations shown in the upper left legend. (B) A dose–response curve of an individual CBZ experiment. The data set belongs to the first light-dark block of Figure 1A. The red crosses/lines represent the light period, whereas the black triangles/lines represent the dark period. The X-axis shows the CBZ dose range (µM) in log scale, whereas the Y-axis shows the time (s) spent in activity within 1 min. Each small symbol shows the time (s) spent in activity by each of the individual 12 replicate embryos within 1 min, while the large symbol represents the geometric means of n = 12 together with their confidence intervals (error bars). |
|
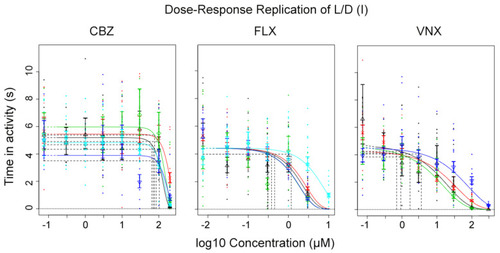
A dose–response curve plot showing five combined replicates of CBZ and FLX and four combined replicates of VNX (dark periods only). The individual experiments were used as covariate. One replicate of each compound was performed at VU, the others at RIVM. Symbols and error bars as in Figure 1B. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
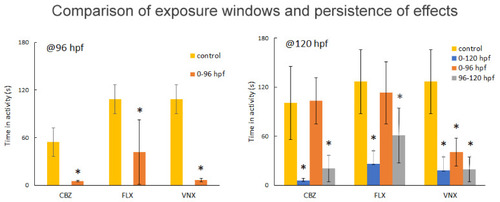
Persistence of effect on activity. Average total activity during the first 10’ dark period of n = 12 embryos, measured at 96 (left) and 120 (right) hpf, following exposure to 200 µM CBZ, 10µM FLX, and 300 µM VNX. The second and third dark block (not shown) provide identical results, whereas the light blocks (not shown) did not show statistical differences compared to the control. The activity (Y-axis) was measured as cumulative duration of movement (in seconds) during 10′. Bar colours indicate different exposure frames (see upper legend). The asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference compared to the control group (p < 0.05); error bars, SD. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Effects of test compounds on marker gene expression. Gene expression analysis after 120 h of exposure to 115 µM CBZ, 107 µM VNX, and 6 µM FLX. The results are the average of n = 6 pools of embryos (each pool containing 12 embryos), expressed by using the delta–delta cycle threshold method (2–∆∆Ct). The asterisk (*) indicates significance, p < 0.05. Error bars, SD. |
|
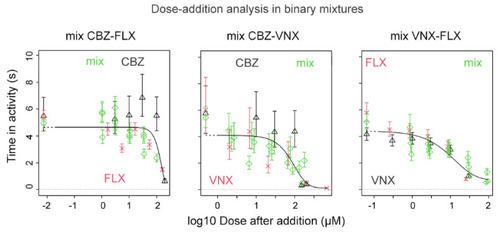
Dose–response mixture effects on swimming activity in zebrafish embryos upon exposure to a mixture of CBZ and FLX, CBZ and VNX, and VNX and FLX. The reference compound (black triangles/lines) is combined with the second compound (red crosses/lines); green diamonds/lines represent the corresponding mixtures. Doses of the second compound and of the mixtures are scaled to the reference compound. The mixtures do not deviate systematically from the overall fit, indicating that the combined effect results from dose addition. PHENOTYPE:
|