|
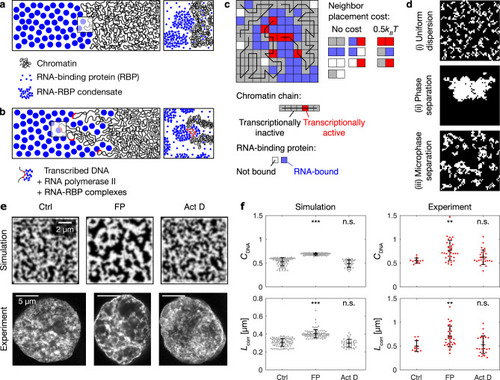
RNA accumulation establishes euchromatin domains, which are maintained in a finely dispersed pattern by transcriptional activity.a Cartoon representation of conventional phase separation and a microemulsion. Right panel focuses on the amphiphile in the microemulsion. b Representative micrographs of nuclear mid-sections obtained from cells treated for 30 min with the indicated inhibitors. The same results were obtained in two independent experiments. c Quantification of DNA image contrast (CDNA) and correlation length (Lcorr) for the different inhibitor treatments: control treatment (Ctrl), flavopiridol (FP), actinomycin D (Act D). Mean ± SD, ** indicates P < 0.01, n.s. indicates P ≥ 0.05 (CDNAP values 0.002, 0.22 from a two-sided permutation test, LcorrP values 0.007, 1.2 from a two-sided permutation test, P values with Bonferroni correction for multiple testing, n = 12,34,29 nuclei from four, three, four different samples). d Representative nuclear mid-section of a flavopiridol-treated cell. The same results were obtained in three independent experiments. e 2D histogram displaying the frequency of pixel-level RNA intensity (IRNA) and DNA intensity (IDNA). Solid and dashed lines are median and 25th and 75th percentile, respectively. f Quantification of CDNA and Lcorr in flavopiridol-treated cells with low and high levels of RNA (the threshold for high RNA is IRNA = 0.25). Mean ± SD, * indicates P < 0.05 (P value 0.03 from a two-sided permutation test, n = 9,62 from five different samples). g Running average (mean ± SEM), window width 0.1, windows with n ≥ 30 nuclei are drawn. h Sketch summarizing the experimental observations to this point. Microscopy data in b–f obtained by STED microscopy, g by spinning disk confocal microscopy.
|