- Title
-
Slc39a5-mediated zinc homeostasis plays an essential role in venous angiogenesis in zebrafish
- Authors
- Xia, Z., Bi, X., Lian, J., Dai, W., He, X., Zhao, L., Min, J., Wang, F.
- Source
- Full text @ Open Biol.
|
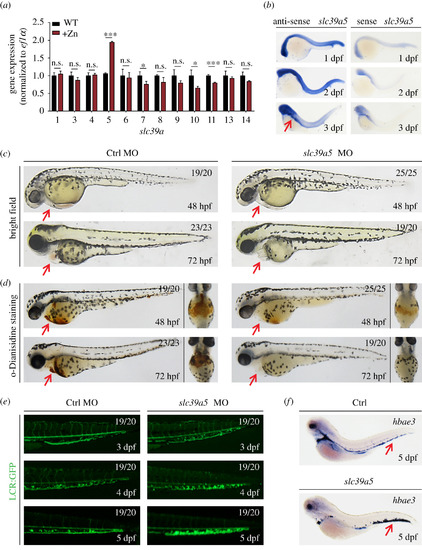
slc39a5 morphant zebrafish embryos develop cardiac ischaemia and blood cell accumulation in the caudal vein plexus. (a) Quantitative PCR analysis of the 12 indicated slc39a genes measured in wild-type (WT) embryos and embryos treated with 1 mM zinc (+Zn). Note zebrafish lacking slc39a2 and slc39a12. (b) In situ hybridization of WT zebrafish embryos using the antisense and sense (control) slc39a5 probes. Note the concentrated expression in the head and gut region at 3 dpf (red arrow). (c–d) Representative images (c) and o-Dianisidine-stained (d) control and scl39a5 morphant embryos at the indicated developmental stages. The red arrows indicate the heart region. (e) Representative images of GFP fluorescence measured in the caudal region of control and slc39a5 morphant Tg(globinLCR:eGFP) embryos. Note the accumulation of RBCs in the CVP of slc39a5 morphants. (f) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of the RBC marker hbea3 in control and slc39a5 morphants. Note the increased signal in the CVP of the slc39a5 morphant (arrow). |
|
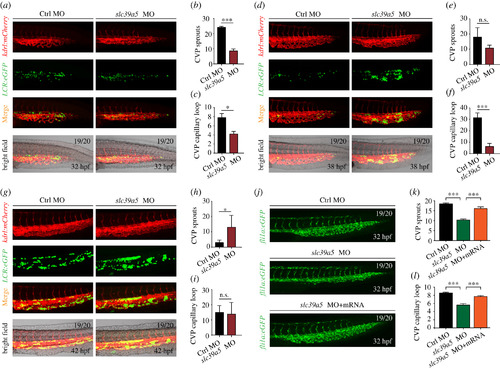
slc39a5 morphants have delayed CVP development. (a–g) Representative images of the caudal region in control and slc39a5 morphant embryos captured using dual-fluorescence microscopy at 32 hpf (a), 38 hpf (d) and 42 hpf (g). The numbers of endothelial sprouts and capillary loops in the CVP were measured at 32 hpf (b–c), 38 hpf (e–f) and 42 hpf (h–i). (j–l) Representative images of the CVP in control Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos and Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos injected with the slc39a5 morpholino alone or co-injected with the slc39a5 morpholino and a morpholino-resistant slc39a5 mRNA. The numbers of endothelial sprouts (k) and capillary loops (l) in the CVP were measured at 32 hpf. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 and n.s., not significant. |
|
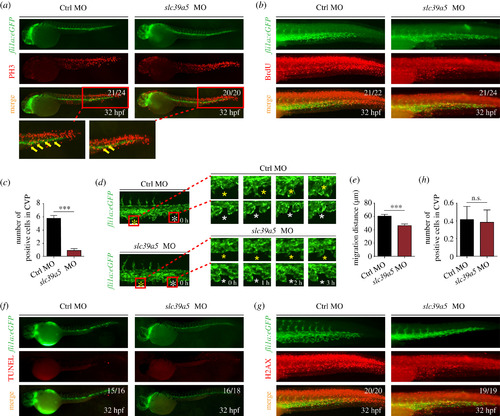
slc39a5 morphants have impaired endothelial cell proliferation and migration in the CVP region. (a–b) PH3 (a) and BrdU (b) immunostaining of control and slc39a5 morphant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos, with magnified views of the CVP showing co-localization of GFP fluorescence and PH3 immunoreactivity (arrows). (c) Summary of BrdU-positive cells in the CVP of control and slc39a5 morphants. ***p < 0.001. (d) Representative sequential images of the CVP in control and slc39a5 morphant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos. For each embryo, two separate endothelial cells are indicated with a white asterisk and a yellow asterisk. Note that 0 h corresponds to 32 hpf. (e) Summary of the migration distance of endothelial cells from 32 to 35 hpf in the CVP of control and slc39a5 morphant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos. (f) Representative images of TUNEL staining in the CVP of control and slc39a5 morphant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos. (g–h) Representative images (g) and summary (h) of H2AX immunostaining in the CVP of control and slc39a5 morphant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
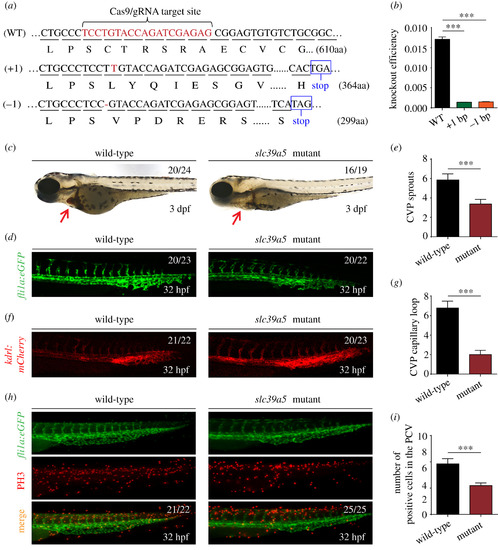
Targeting strategy and characterization of slc39a5 knockout zebrafish. (a) DNA and corresponding amino acid sequences of the wild-type (WT) slc39a5 allele and the slc39a5 allele after inserting one nucleotide (+1) or deleting one nucleotide (−1) using CRISPR/Cas9-based editing. Both the insertion and the deletion introduce a premature stop codon. (b) Summary of slc39a5 mRNA measured using qPRC in the WT, +1, and −1 slc39a5 mutant lines (n = 3 sets of 50 pooled embryos/group). (c) Representative images of a wild-type and mutant embryo at 3 dpf. Note the significantly smaller heart with reduced cardiac blood flow in the mutant embryo (arrow). (d–e) Representative images of the CVP in wild-type (left) and mutant (right) Tg(fli1a:eGFP) (d) and summary of CVP sprouting in these embryos (e). (f–g) Representative images of the CVP in wild-type (left) and mutant Tg(kdrl:mCherry) (f) and summary of capillary loops in the CVP (g) in these embryos. (h) Representative images of PH3 immunostaining in the CVP of wild-type and mutant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos. (i) Summary of PH3-positive cells in the CVP of wild-type and mutant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos at 32 hpf. ***p < 0.001. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |