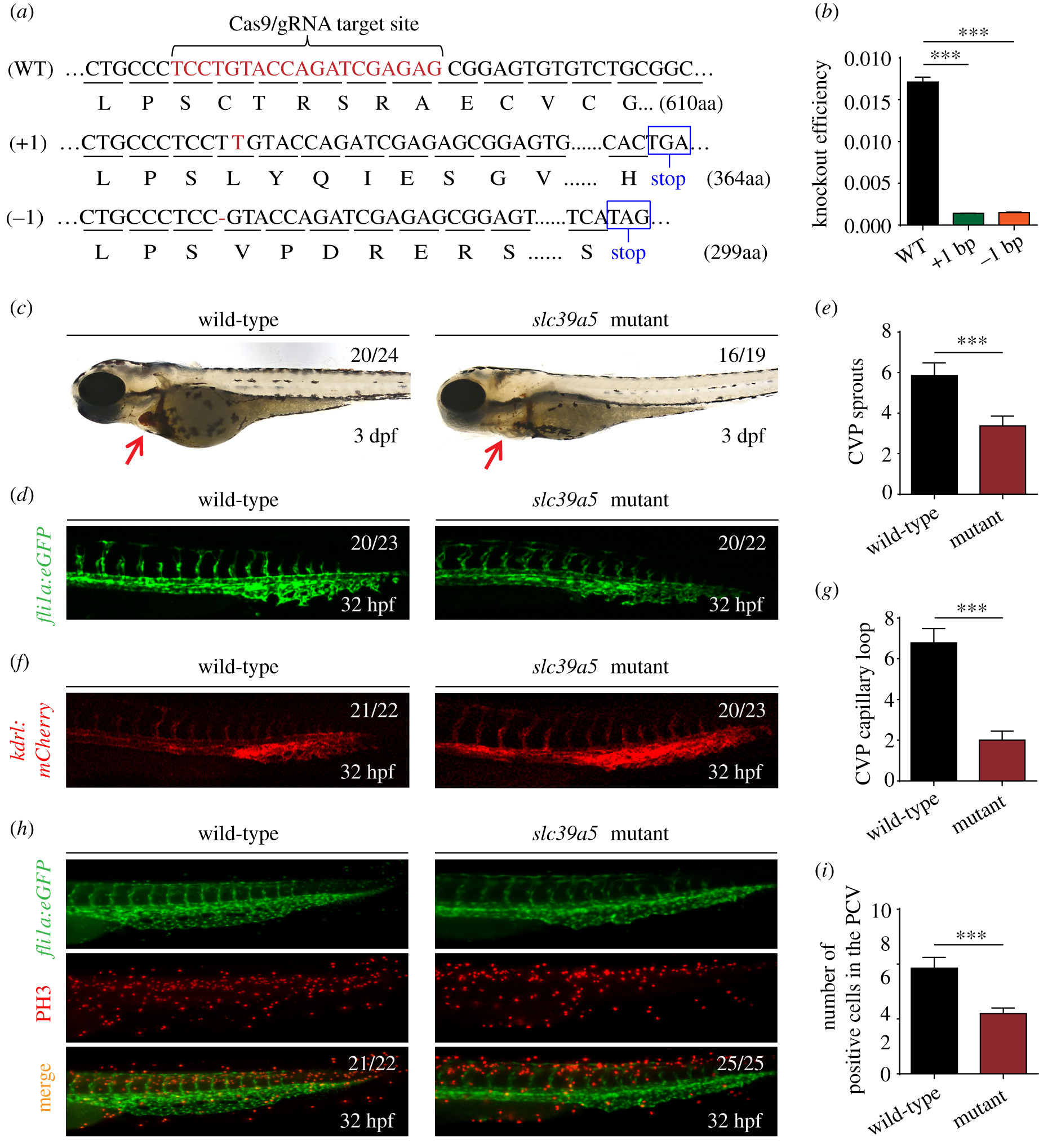
Fig. 4 Targeting strategy and characterization of slc39a5 knockout zebrafish. (a) DNA and corresponding amino acid sequences of the wild-type (WT) slc39a5 allele and the slc39a5 allele after inserting one nucleotide (+1) or deleting one nucleotide (−1) using CRISPR/Cas9-based editing. Both the insertion and the deletion introduce a premature stop codon. (b) Summary of slc39a5 mRNA measured using qPRC in the WT, +1, and −1 slc39a5 mutant lines (n = 3 sets of 50 pooled embryos/group). (c) Representative images of a wild-type and mutant embryo at 3 dpf. Note the significantly smaller heart with reduced cardiac blood flow in the mutant embryo (arrow). (d–e) Representative images of the CVP in wild-type (left) and mutant (right) Tg(fli1a:eGFP) (d) and summary of CVP sprouting in these embryos (e). (f–g) Representative images of the CVP in wild-type (left) and mutant Tg(kdrl:mCherry) (f) and summary of capillary loops in the CVP (g) in these embryos. (h) Representative images of PH3 immunostaining in the CVP of wild-type and mutant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos. (i) Summary of PH3-positive cells in the CVP of wild-type and mutant Tg(fli1a:eGFP) embryos at 32 hpf. ***p < 0.001.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Open Biol.