- Title
-
Zebrafish ambra1a and ambra1b Silencing Affect Heart Development
- Authors
- Meneghetti, G., Skobo, T., Chrisam, M., Fontana, C.M., Facchinello, N., Nazio, F., Cecconi, F., Bonaldo, P., Dalla Valle, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Zebrafish
|
Knockdown of zebrafish ambra1a and ambra1b impairs cardiac development. Representative bright-field images of the cardiac region of 3 dpf live embryos injected with the indicated MOs. ambra1a and ambra1b ATG-morphant embryos show pericardial edema (asterisk) and string-like heart tube when compared to WT and 5M control embryos. No visible abnormalities are evident in splice morphants, whereas cardiac defects are enhanced in the double morphants. The phenotypic defects of ATG-morphant embryos are rescued by co-injection with hAMBRA1 mRNA, but not with the AMBRA1PXP mRNA. The dotted line highlights the heart shape in the different conditions. A, atrium; V, ventricle. Scale bar, 200 μm. Images taken at 10 × magnification. More than 100 embryos observed for each condition, from five independent experiments. AMBRA1, activating molecule in beclin-1 (BECN1)-regulated autophagy; dpf, days postfertilization; hAMBRA1, human AMBRA1; MOs, morpholino oligonucleotides; mRNA, messenger RNA; WT, wild type. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
AMBRA1 silencing in zebrafish causes aberrant cardiac looping and laterality defects. (A) Representative WMISH images for myl7 in WT and ambra1a and ambra1b ATG-morphant embryos at 20, 24, and 36 hpf developmental stages. The expected position and shape of the developing heart at the respective developmental stages are depicted in the schematic diagram on the left. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) Dorsal views of the lateral plate mesoderm of WT and ambra1a and ambra1b ATG-morphant embryos at 19 hpf, showing different pitx2c expression patterns, as indicated by the arrowheads. Morphant embryos display disorganization of the presumptive localization of Rohon-Beard neurons (depicted in the schematic diagram on the right). Scale bar, 200 μm. n = 30 embryos for each condition. hpf, hours postfertilization; myl7, myosin light chain 7; pitx2c, homeodomain transcription factor 2 isoform c; WMISH, whole-mount in situ hybridization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
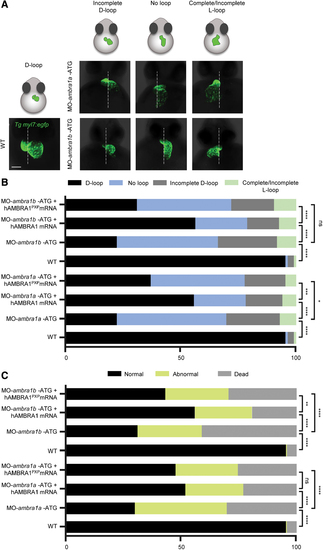
Characterization of the heart looping phenotypes following AMBRA1 silencing in the myl7:EGFP zebrafish transgenic line. (A) Three-dimensional reconstructions of WT and ambra1a and ambra1b ATG-morphant hearts expressing the myocardial reporter transgene myl7:EGFP at 48 hpf. The panels show the various types of abnormal looping phenotypes found in morphants (incomplete D-loop, no loop, and complete/incomplete L-loop), in addition to the normal D-looping orientation of WT hearts. The dotted white line marks the midline axis of the embryos. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) Percentage of D-loop, incomplete D-loop, complete or incomplete L-loop, and no-loop orientation of the developing heart at 48 hpf in WT embryos, AMBRA1 morphant embryos, and AMBRA1 morphant embryos co-injected with hAMBRA1 or mutated hAMBRA1PXP mRNAs. (C) Percentage of normal, abnormal, and dead 48 hpf embryos in the different conditions as above. For each condition, 200 embryos were analyzed. Statistical analysis was performed by chi-squared test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. hAMBRA1PXP, human AMBRA1 mRNA mutated in the protein phosphatase 2a (PP2A) binding sites; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; ns, not significant. Color images are available online. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
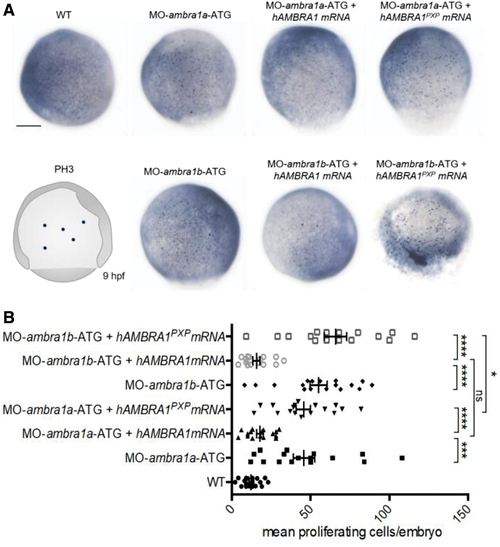
AMBRA1 morphant embryos display increased cell proliferation. (A) Representative images of phospho-histone H3 immunohistochemistry in WT and AMBRA1 morphant embryos at 9 hpf. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) The numbers of proliferating cells were counted and compared between WT embryos, AMBRA1 morphant embryos, and AMBRA1 morphant embryos co-injected with hAMBRA1 or mutated hAMBRA1PXP mRNAs. For each condition, 10 embryos were analyzed, and the experiment was performed twice. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t-test. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. Color images are available online. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
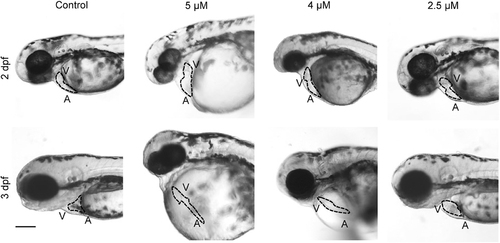
Treatment with a PP2A-specific inhibitor causes defective heart development in zebrafish. Representative bright-field micrographs of the cardiac region of 2 and 3 dpf live embryos treated with the indicated concentrations of the PP2A inhibitor cantharidin. The dotted line highlights the heart shape in the different conditions. Scale bar, 200 μm. A, atrium; V, ventricle. n = 30 embryos for each condition, from three different experiment. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Ambra1 knockout affects heart development also in mouse. Statistical analysis of the penetrance of heart phenotype in Ambra1gt/gt embryos of different genetic strains (A). Hematoxylin/eosin staining on sections of E13.5 embryos (B). Ambra1gt/gt embryos display thinner walls of cardiac muscle (short arrows) and no difference in thickness of the trabecular layer (long arrows). At this stage, mouse embryos displayed disorganization of the ventricular trabeculae. Scale bar, 200 μm. Color images are available online. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|